When the Fed injected newly made money into the economy by buying bonds, it:
A. was practicing quantitative easing.
B. was trying to avoid a deflationary period similar to Japan.
C. inserted over $1 trillion of new money into the economy.
D. All of these statements are true.
D. All of these statements are true.
You might also like to view...
The real interest rate bringing the supply of saving equal to the demand for saving is an example of the:
A. cost-benefit principle B. equilibrium principle. C. scarcity principle. D. principle of increasing opportunity cost.
Assuming the economy in the graph shown is currently at equilibrium A, we can conclude:
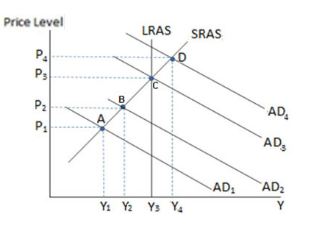
A. the economy is in a recession.
B. the economy is producing less than its potential level of output.
C. there must be unemployment of resources.
D. All of these are true.
The structural deficit does not depend on the state of the economy
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Aggregate demand is reduced by
A. increased government spending. B. reduced taxes. C. decreased interest rates. D. a stronger dollar.