Refer to the graph shown. Assume the economy is in short-run equilibrium at point A below potential output. The government opts for an expansionary fiscal policy in an attempt to pull the economy out of the recession. An economist with a Classical view holding the Ricardian equivalence theorem to be practically true would conclude that the economy will most likely end up at point: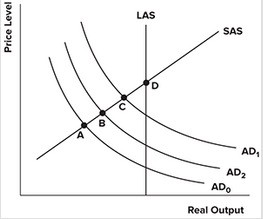
A. A.
B. B.
C. C.
D. D.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
The deadweight loss due to a ________ is always smaller than the deadweight loss due to a ________
A) tax on each unit sold; per unit tax on each unit bought B) per unit tax on each unit sold; per unit tax on each unit bought C) tax on each unit sold; lump-sum tax D) lump-sum tax; tax on each unit bought
Explain how menu costs affect the slope of the short-run aggregate supply curve
What will be an ideal response?
If some firms leave a monopolistically competitive market, the
a. remaining firms will charge a lower price to try to capture the released market share b. remaining firms' cost curves will shift upward and to the right c. remaining firms' demand curves will shift to the left d. market demand curve shifts to the right e. remaining firms will produce at a different point on their ATC curves
A decrease in the price of bubble gum below equilibrium will
A. Shift the bubble gum demand curve to the right. B. Cause a shortage of bubble gum. C. Cause a surplus of bubble gum. D. Shift the bubble gum supply curve to the right.