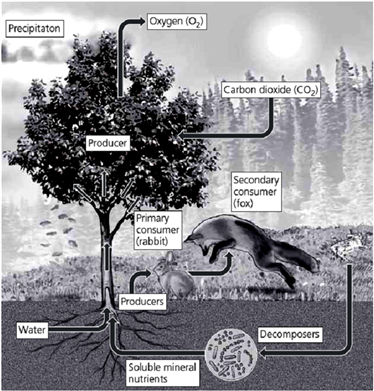
Figure 3.5 Key living (biotic) and nonliving (abiotic) components of an ecosystem in a field.
?
In the accompanying figure, notice that the fox (secondary consumer) is in the process of pouncing on the rabbit. If humans were to remove that predator (fox), what would be the effects on the rest of the ecosystem? Be as specific as possible.
What will be an ideal response?
The loss of a predator in an ecosystem results in an imbalance in the system. The primary consumer is freed from the environmental pressure of predation and increases its population. The increased population puts additional pressure on the producers, potentially reducing their viability. The rabbit's food source will eventually decline, possibly resulting in increased death in the rabbit population. Decomposers will have additional food sources and may increase in population. Other prey populations, held in check by the fox, may also experience the same changes.
You might also like to view...
Explain why locating industrial facilities on the perimeter of a city might not always prevent air pollution in the city.
What will be an ideal response?
A change in the acidity of mountain lakes would most likely be a result of
(1) ecological succession of the area at the top of the mountain (2) the introduction of new species into the lakes (3) air pollution from smoke stacks miles away (4) planting grasses and shrubs around the lakes
In the late 1800s, the majority of immigrants to the United States came from
A. Eastern and Southern Europe B. Northern and Western Europe C. Asia D. Africa
Rare-earth elements are a necessary component in the production of electric- and hybrid-automobiles. Indicate whether the statement is true or false