The table below shows the aggregate demand and aggregate supply schedules for a hypothetical economy.
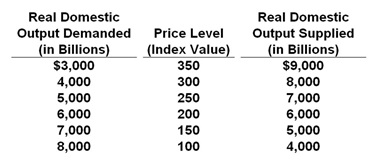
Refer to the table above. At the price level of 150, there will be a general:
A. Surplus in the economy, and output supplied will decrease as the price level falls
B. Shortage in the economy, and output demanded will decrease as the price level rises
C. Surplus in the economy, and output supplied will increase as the price level rises
D. Shortage in the economy, and output demanded will increase as the price level falls
B. Shortage in the economy, and output demanded will decrease as the price level rises
You might also like to view...
Consider three pricing strategies that the firm can pursue:
a. optimal two-part tariff pricing b. perfect price discrimination c. single-price monopoly pricing. Of these three strategies, which is least likely to benefit society as a whole? A) single-price monopoly pricing because there are mutually beneficial trades (between consumers and seller) that are not exploited B) Both perfect price discrimination and two-part tariff pricing do not benefit society because the entire consumer surplus is extracted by the producer. C) perfect price discrimination because those willing to pay higher prices are forced to subsidize those who are not D) a two-part tariff pricing because consumers have to pay a fixed fee in addition to a per-unit price
A technological breakthrough that increases the marginal productivity of capital would increase the
a. demand for loanable funds, leading to a lower equilibrium market interest rate b. supply of loanable funds, leading to a lower equilibrium market interest rate c. demand for loanable funds, leading to a higher equilibrium market interest rate d. supply of loanable funds, leading to a higher equilibrium market interest rate e. supply of loanable funds but have no impact on the equilibrium market interest rate
The prevalent welfare policy is to
A. provide vocational training for welfare recipients, so that they can be self-supporting. B. provide government and private sector employment for those leaving the welfare rolls. C. to basically force welfare recipients to leave the welfare rolls. D. to allow welfare recipients to continue receiving benefits as long as there are children under six years of age in the family.
Assuming there are no externalities, if a firm is producing at an output level where the benefits to consumers are less than the cost to the suppliers to produce it, then price
A. is less than marginal cost. B. is greater than marginal cost. C. is less than marginal revenue. D. equals marginal cost.