Suppose the price of one euro is fixed at $1.00. A Dutch oil company discovers new oil reserves in the North Sea and offers the oil for sale. What is the result if a flexible exchange rate is allowed?
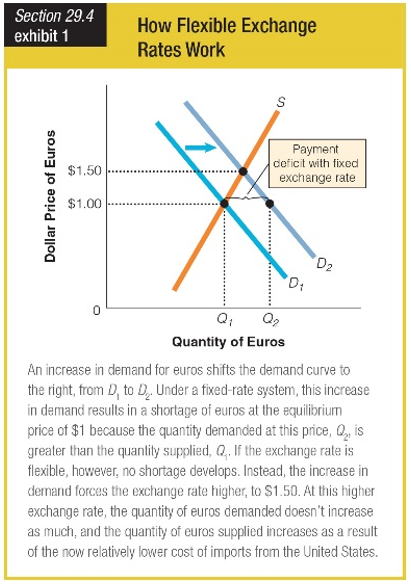
a. The euro changes in value from $1.00 per euro to an equilibrium price of $1.50 per euro.
b. European goods become more expensive to U.S. residents, moving Q2 to Q1.
c. The euro changes in value from $1.50 per euro to an equilibrium price of $1.00 per euro.
d. U.S. exports become cheaper to Europeans, moving Q2 to Q1.
a. The euro changes in value from $1.00 per euro to an equilibrium price of $1.50 per euro.
You might also like to view...
Refer to Figure 7-2. The tariff causes domestic consumption of coffee
A) to rise by 20 million pounds. B) to fall by 27 million pounds. C) to rise by 6 million pounds. D) to fall by 7 million pounds.
If American and Japanese consumers buy the same basket of goods in each country and there is no inflation in either country,
A) the law of one price will hold. B) deviations from PPP will occur. C) PPP will hold. D) Both A and C.
The reason that patents are granted is
A) to encourage a high rate of consumption. B) to protect new techniques developed through research and development. C) to encourage free trade. D) to increase the labor force.
Under the Fed's current interest-rate-targeting approach to monetary policy, if the demand for federal funds by depository institutions increases today, then, other things being equal
A) the market federal funds rate decreases, and the Fed's Trading Desk responds by selling bonds. B) the market federal funds rate increases, and the Fed's Trading Desk responds by buying bonds. C) the market federal funds rate decreases, and the Fed's Trading Desk responds by buying bonds. D) the market federal funds rate increases, and the Fed's Trading Desk responds by selling bonds.