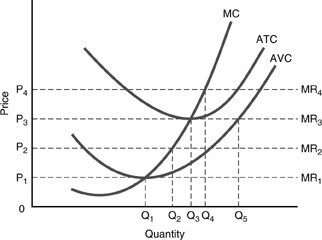
 Using the above figure, the price facing the perfectly competitive firm in the long run will be
Using the above figure, the price facing the perfectly competitive firm in the long run will be
A. P1.
B. P2.
C. P3.
D. P4.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
The 2001 and 2003 tax cuts of the George W. Bush administration each had provisions to
A. phase out the estate tax. B. lower the earned income tax credit. C. raise tax rates at the lower end. D. raise tax rates at the upper end.
The Granger Causality Test
A) uses the F-statistic to test the hypothesis that certain regressors have no predictive content for the dependent variable beyond that contained in the other regressors. B) establishes the direction of causality (as used in common parlance) between X and Y in addition to correlation. C) is a rather complicated test for statistical independence. D) is a special case of the Augmented Dickey-Fuller test.
It costs a firm $80 per unit to produce product A and $50 per unit to produce B individually. If the firm can produce both products together at $120 per unit of product A and B, this exhibits signs of
a. Economies of scale b. Economies of Scope c. Diseconomies of Scale d. Diseconomies of Scope
In practice, distribution under socialism is primarily determined by:
A. the ability of each individual to produce. B. individual altruism and cooperation. C. central planners within the government. D. market forces of supply and demand.