The change in saving divided by the change in income is the
a. ratio of saving to income
b. same as saving divided by income
c. average propensity to save
d. marginal propensity to consume
e. marginal propensity to save
E
You might also like to view...
Answer the following statement(s) true (T) or false (F)
1. A non-congested toll road is an example of a good that is excludable, but not rivalrous in consumption. 2. Public goods can frequently be provided by private action when the resulting benefits are widespread. 3. All economists agree that a public good is one the is nonrivalrous and nonexcludable. 4. When a public goods increases the desirability of living in a certain area, benefits tend to be captured entirely by an increase in land values. 5. In a Clarke tax scheme, the amount of tax that a person pays depends, in part, on his revealed preference for the public good.
Which statement is true?
A. The recessions of 1973-1975 and 1981-1982 were both mild. B. The recessions of 1973-1975 and 1981-1982 were both severe. C. The recession of 1973-1975 was mild; the recession of 1981-1982 was severe. D. The recession of 1973-1975 was severe; the recession of 1981-1982 was mild.
Figure 11-9
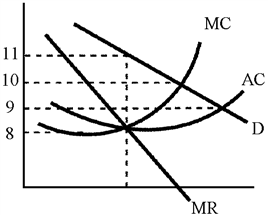
In Figure 11-9, how much more than the short-run competitive price will the profit-maximizing monopolist charge?
a.
$1
b.
$2
c.
$3
d.
$10
The economy experiences an increase in the price level and a decrease in real domestic output. Which of the following is a likely explanation?
A. Productivity has increased B. Input prices have increased C. There has been an increase in government spending D. Government regulations have been reduced