Government fiscal policies that attempt to stimulate aggregate demand are often aimed at reducing cyclical unemployment
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
True
You might also like to view...
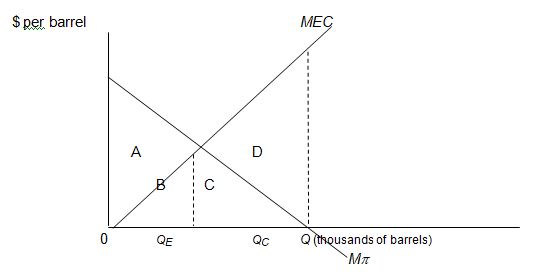
Which area represents the net gain to society? Should the reduction in output from QC to QE take place? Why or why not?
Use the following graph of the refined petroleum market to answer the questions below.
Your neighbor has just planted some fragrant flowers. The wonderful scent drifts into your room and makes you happy
A) This scent is an internal cost to you. B) This cannot be an externality since you are enjoying the scent. C) This is an externality since you get a benefit from your neighbor's flowers. D) The social cost of this activity is entirely borne by you neighbor.
Assume that the expectation of declining housing prices cause households to reduce their demand for new houses and the financing that accompanies it. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a flexible exchange rate system, what happens to the real risk-free interest rate and GDP Price Index in the context of the Three-Sector-Model?
a. The real risk-free interest rate and GDP Price Index remain the same. b. The real risk-free interest rate falls, and GDP Price Index falls. c. The real risk-free interest rate falls, and GDP Price Index stays the same. d. The real risk-free interest rate rises, and GDP Price Index falls. e. The real risk-free interest rate rises, and GDP Price Index rises.
Exhibit 2-10 Production possibilities curve data A B C D E Capital goods 0 1 2 3 4 Consumption goods25 23 19 13 0 Suppose an economy is faced with the production possibilities table shown in Exhibit 2-10. As additional units of capital goods are being produced, the number of consumption goods produced must:
A. increase because the production possibility table shows only the maximum efficiency points. B. increase because of the law of increasing costs. C. decrease because of the law of increasing costs. D. decrease because of the finite nature of the resource base.