In a two good, two-country world, a country has a comparative advantage in any good for which it has a:
a. lower absolute cost than the other country.
b. lower opportunity cost than the other country.
c. higher absolute cost than the other country.
d. higher opportunity cost than the other country.
b
You might also like to view...
Refer to the scenario above. If the rules of the gamble are changed such that in the case of heads, the individual wins $50, and in the case of tails, the individual loses $100, the expected value of the gamble changes to:
A) $25. B) -$25. C) $50. D) -$50.
If the accounting profit equals $200,000 and implicit costs equal $40,000, the economic profit equals
a. $240,000. b. $200,000. c. $160,000. d. $40,000.
Which of the following may lead to diseconomies of scale?
a. Specialization on the basis of comparative advantage b. Lack of coordination among the division heads c. Using larger and more efficient machineries d. Division of labor on the basis of capability e. Specialization of marketing, pricing, and research
What is Calvin’s opportunity cost to produce 3/4 pound of food?
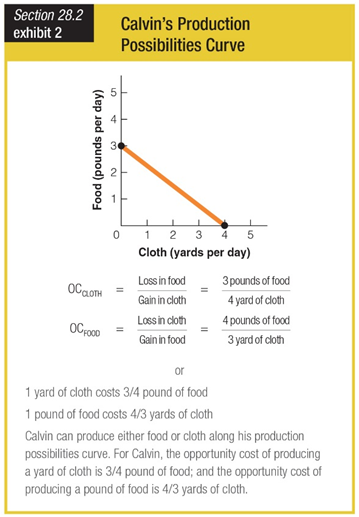
a. 1/2 yard of cloth
b. 1 yards of cloth
c. 1-1/2 yards of cloth
d. 2 yards of cloth