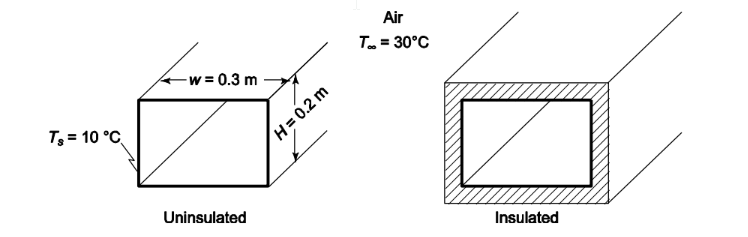
Cooled air is flowing through a long sheet metal air conditioning duct, 0.2 m high and 0.3 m wide. If the duct temperature is 10°C and passes through a crawl space under a house at 30°C, estimate
(a) The heat transfer rate to the cooled air per meter length of duct.
(b) The additional air conditioning load if the duct is 20-m-long.
(c) Discuss qualitatively the energy conservation if the duct were insulated with glass
wool.
GIVEN
• An air conditioning duct in a crawl space
• Duct height (H) = 0.2 m
• Duct width (w) = 0.3 m
• Duct temperature (Ts) = 10°C
• Ambient temperature (T?) = 30°C
FIND
(a) The heat transfer rate per meter length (qc/L) to the cooled air in the duct
(b) The additional air conditioning load (q20) if the duct length (L) = 20 m
(c) Discuss qualitatively the energy conservation if the duct were insulated with glass wool
ASSUMPTIONS
• Ambient air is still
• Duct temperature is constant and uniform
• Radiation is negligible
• Edge effects are negligible
• No condensation on the duct surface
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for dry air at the mean temperature of 20°C
Thermal expansion coefficient (?) = 0.00341 1/K
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0251 W/(m K)
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 15.7 × 10–6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71
(a) The duct can be thought of as two vertical and two horizontal cooled flat plates.
For the sides
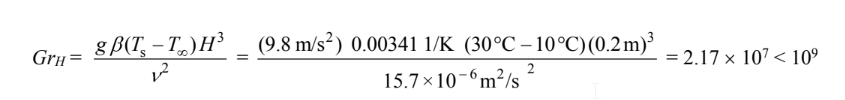
So the flow is laminar.
For the top and bottom, the characteristic length (Lc) is given by
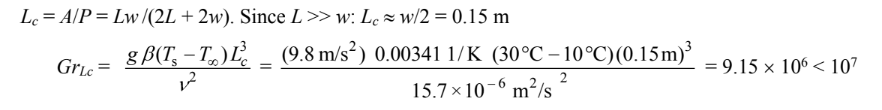
The heat transfer coefficient for the vertical sides of the duct is given by
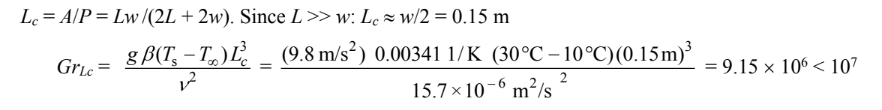
The top is a cooled surface facing upward. The heat transfer coefficient from the top is the same as that for a heated surface facing downward and given by
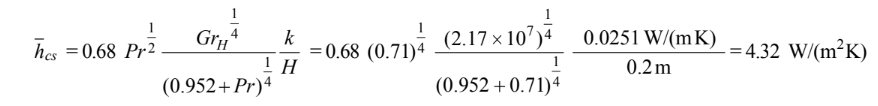
The heat transfer coefficient for the bottom, a cooled surface facing downward, is given by
since RaL < 107

The total convective heat transfer to the duct is

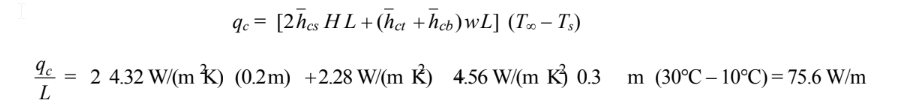
(b) For a 20-m-long duct

(c) The addition of insulation to the outer surface of the duct will have several effects
1. It will increase the outer surface temperature of the duct and decrease the duct wall
temperature.
2. The higher surface temperature will lower the natural convection heat transfer coefficient
because the temperature difference between the duct and the ambient air will be reduced.
3. The lower convective heat transfer coefficient and the additional conductive thermal
resistance of the insulation will lead to a decrease in the rate of heat transfer to the air in the duct. This will reduce the load on the air conditioning system assuming that the crawl space is not to be intentionally cooled.
You might also like to view...
Which galaxy, as observed, has aged the most since it was born?
A) a very distant galaxy B) a nearby galaxy C) The distance of a galaxy doesn't matter.
Carbon dioxide and water molecules in the atmosphere will absorb:
a. infrared light. c. ultraviolet light. b. visible light. d. radio waves.
Suppose we take a disk of radius R and remove the material from r = 0 to r = R, making a hole at the center of the disk. Note that this decreases the mass of the disk. Will the value of ? for the new object be larger, smaller, or the same as that for the original object?
A. The value of ? will be larger for the new object. B. The value of ? will be smaller for the new object. C. The value of ? is the same for both objects. D. We need to know the disk’s thickness to answer.
Arrange the following distances in order from smallest to largest. I. kilometer II. light-year III. yard IV. astronomical unit
a. I, II, III, IV b. IV, III, II, I c. III, I, IV, II d. II, I, IV, III e. III, I, II, IV