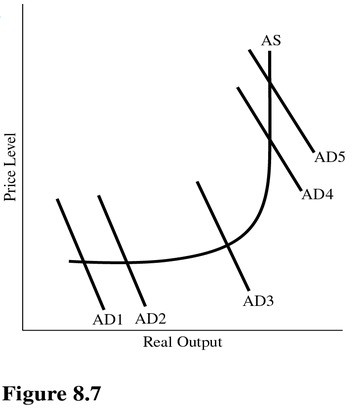
 Using Figure 8.7, a shift in aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2 is most likely to cause
Using Figure 8.7, a shift in aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2 is most likely to cause
A. An increase in price level but no change in real output.
B. A decrease in price level but no change in real output.
C. An increase in real output but no change in the price level.
D. An increase in real output and an increase in the price level.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Esther wants to buy a used car from her neighbor, who quotes a price of $18,000. Esther negotiates with her neighbor and offers him $16,500 for the car. This is an example of ________
A) bilateral bargaining B) collective bargaining C) arbitration D) speculation
You are the liaison between the Federal Reserve Board and the U.S. Treasury Department. Your goal is to coordinate policy efforts to achieve full-employment output in the economy while keeping a fixed real interest rate
You must recommend tightening or easing both monetary and fiscal policies to do this. What would your recommendation be in each of the following situations? (a) People decide to increase saving. (b) Expected inflation declines. (c) The future marginal productivity of capital declines. (d) There's an adverse oil price shock in which the LM curve moves farther to the left than does the FE line.
Sweep accounts which were created to avoid reserve requirements became possible because of a change in
A) deposit ceilings. B) technology. C) government rules. D) bank mergers.
If the price of hot dogs increases, what will happen in the market for potato chips, a complementary good?
a. Demand will increase. b. Quantity demanded will increase. c. Demand will decrease. d. Quantity demanded will decrease. e. Supply will decrease.