Refer to Figure P2.27 and assume that vS = 15 V and RS = 100 ?. For iT = 0, 10, 20, 30, 80, and 100 mA:
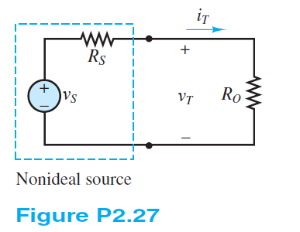
a. Find the total power supplied by the ideal source.
b. Find the power dissipated within the non-ideal source.
c. How much power is supplied to the load resistor?
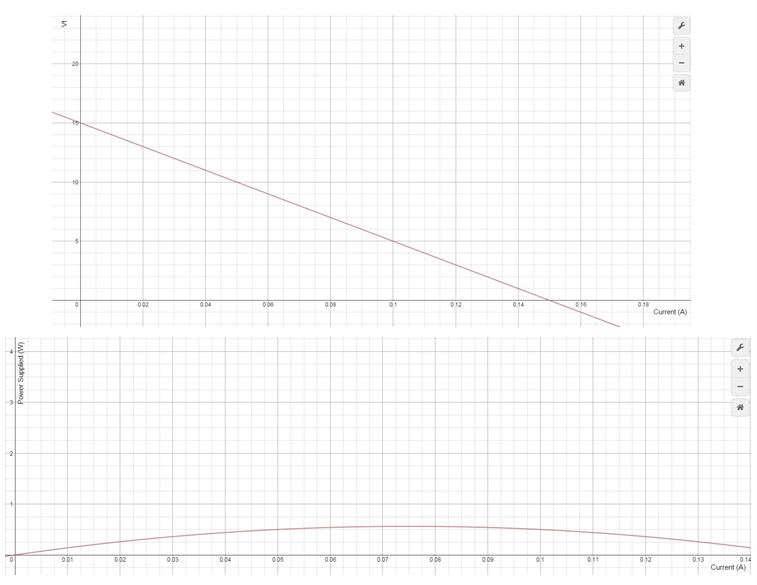
d. Plot the terminal voltage vT and power supplied to the load resistor as a function of terminal current iT .
a) The power supplied by the ideal source is equal to the current through the loop times the 15V of the supply. From current lowest to highest the power supplied would be:
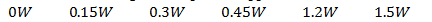
b) The power dissipated within the non-ideal source is the power dissipated by Rs which can be found using P=i2*r. From current lowest to highest the power dissipated would be:

c) The power supplied to the load resistor is equal to the total power supplied minus the power dissipated by the non-ideal source. From current lowest to highest the power supplied would be:

d) For the vT plot Ohm’s Law can be used to find the voltage drop across Rs which is vT = 15 – 100iT. For the power plot, the data from part c can be used directly.
You might also like to view...
Building codes typically specify five general types of construction, which are represented by the decimal numerals 1 through 5.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
A flammable liquid's ____________________ is the temperature at which the vapors will ignite when brought into contact with an open flame.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
A design brief encourages thinking about only one aspect of a problem before attempting a solution.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Electricity that is in motion with a current flow is referred to as:
A) Dynamic electricity. B) Potential energy. C) Static electricity. D) Hyperbolic electricity.