The main function of dense regular connective tissues is
a) storing minerals for later use.
b) forming stroma of soft organs.
c) reducing heat loss from the body surface.
d) providing strong attachment between structures like muscle and bones.
e) providing elasticity to stretchable organs.
Answer: d
You might also like to view...
Using Figure 24.2, match the following:
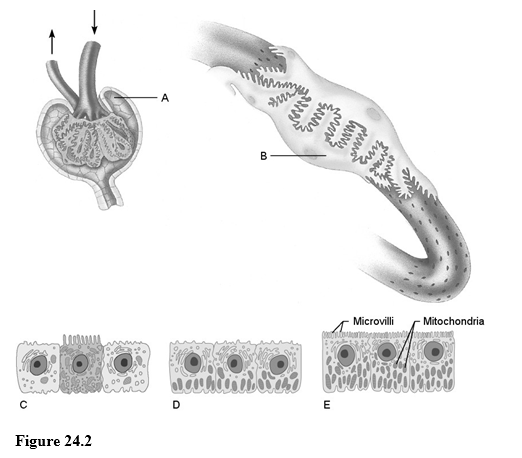
1) Podocyte.
2) Is composed of simple squamous epithelium.
3) Collecting duct cells.
4) Proximal convoluted tubule cells.
5) Filtrate at the site of these cells is about the same osmolarity as blood plasma.
6) Cells that are the most active in reabsorbing the filtrate.
7) Cells that reabsorb virtually all the nutrients.
8) Cells that are most affected by ADH.
9) Almost no water is absorbed in these cells.
Sodium chloride is considered a(n)
A. molecule. B. element. C. compound. D. molecule and a compound. E. ion.
When sodium is actively transported from tubular cells to the interstitial fluid,
A. no energy is needed. B. glucose and amino acids are countertransported at the same time. C. Na+ concentration gradient is established between the tubule lumen and tubule cell. D. water is countertransported by carrier molecules. E. water is secreted.
Which of the following describes inspiratory reserve volume?
A. The amount of air that can be forcefully expired beyond the amount expired in a normal breath at rest B. The amount of air moved in a normal breath (inspired or expired) at rest C. The amount of air that can be forcefully inspired beyond the amount inspired in a normal breath at rest D. The amount of air in the lungs that cannot be moved