Selection bias is a problem when trying to estimate the return to education in a standard human capital model. In this context, what does selection bias refer to?
A. Colleges select who they are willing to accept.
B. The data sample is nonrandom.
C. The wage-schooling locus does not have a constant slope.
D. The wage-schooling locus is estimated to have a negative slope.
E. Workers self-select education levels and jobs based on their abilities and preferences.
Answer: E
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, an increase in government spending that increases aggregate demand from AD to AD1 will lead to a short-run equilibrium at point ________ creating _____gap. 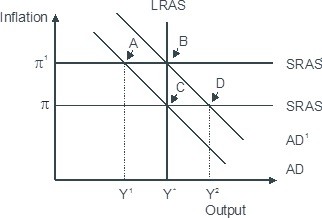
A. D; an expansionary B. B; no output C. B; expansionary D. A; a recessionary
If household saving decreases by $3 million, business saving increases by $1 million, and the government budget deficit increases by $2 million, then private saving ________ and public saving ________.
A. decrease; decreases B. increases; decreases C. does not change; increases D. increases; does not change
The marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is the
A) fraction of additional income that is spent. B) fraction of additional consumption that is not based on the level of income. C) ratio of consumption to savings. D) ratio of consumption to income.
The quantity theory of money and prices
A) is derived from the equation of exchange assuming that prices remain constant. B) shows how a change in the price level leads to a change in the money supply. C) shows how the demand for money is inversely related to the price level. D) is the hypothesis that changes in the money supply leads to proportional changes in the price level.