If a firm facing a perfectly elastic demand curve raises its price,
a. it will still sell exactly the same amount of output as it did at the lower price
b. it will lose some, but not all, of its sales
c. its sales will decrease to zero
d. its sales will increase
e. it is impossible to predict what will happen to its sales
C
You might also like to view...
Cost-of-service regulation allows regulated companies to charge prices that
A) reflect the cost of regulating the industry, plus the marginal cost of the product. B) allow monopoly profits to the producer. C) reflect the actual average cost of providing the services to the customer. D) are determined by competition in other geographic markets.
What are the policies usually advocated by supply side economists? How do they justify these proposals?
Suppose Firm A and Firm B are considering whether to invest in a new production technology. For each firm, the payoff to investing (given in thousands of dollars per day) depends upon whether the other firm invests, as shown in the payoff matrix below.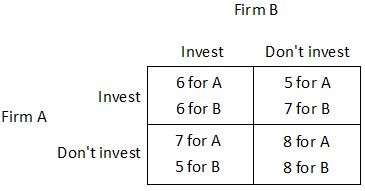 Is this game a prisoner's dilemma?
Is this game a prisoner's dilemma?
A. No. B. Yes. C. It cannot be determined. D. Only when both Firm A and Firm B invest.
When looking at this graph for the welfare effects of a subsidy, which area represents the cost of the subsidy to the government?
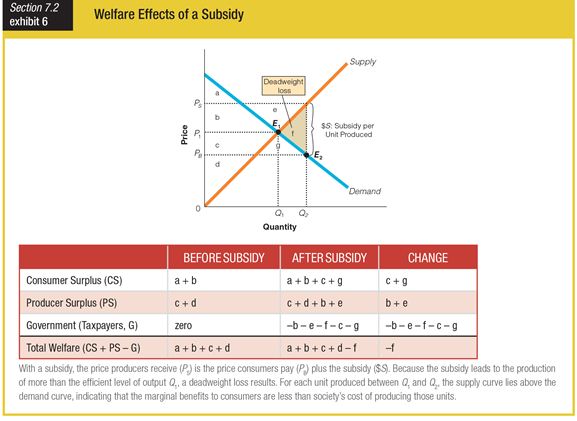
a. area a + b + c + d
b. area b + e + f + c + g
c. area f
d. area a + b – c