Refer to Figure 8.6, which shows a firm's short-run average cost curves for three different levels of capital. Which of the following statements about short-run and long-run marginal cost is true?
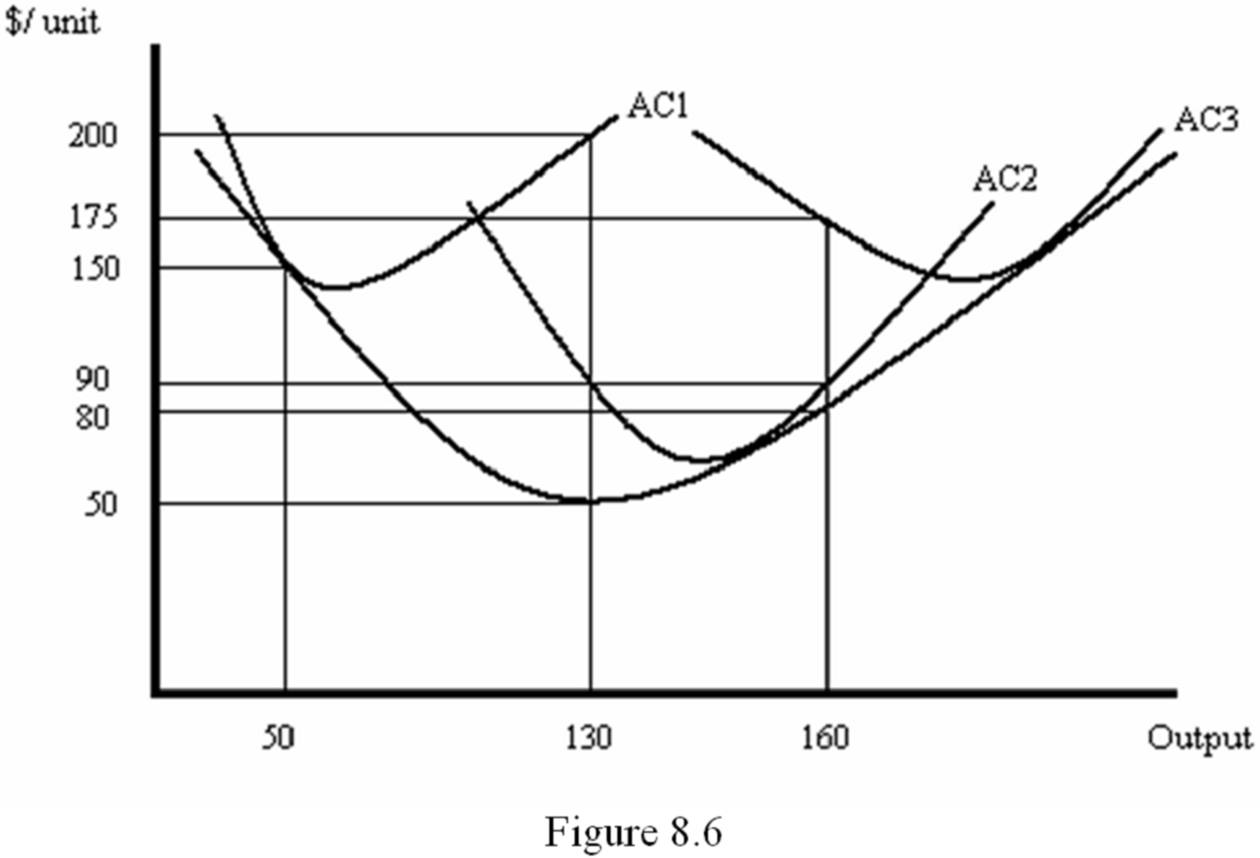
A. Long-run marginal cost equals short-run marginal cost at 50 units of output.
B. Long-run marginal cost equals short-run marginal cost at 130 units of output.
C. Long-run marginal cost equals short-run marginal cost at 160 units of output.
D. Long-run marginal cost and short-run marginal cost are never equal.
A. Long-run marginal cost equals short-run marginal cost at 50 units of output.
You might also like to view...
The following data relate to the supply schedule of a product.PriceQuantity Supplied$51001020015250203002535030500Using the regular percentage change formula, what is the price elasticity of supply when price decreases from $10 to $5?
A. 0.2 B. 0.5 C. 0.6 D. 1
The Walt Disney Company is in a position to use a two-part tariff by charging for admission and also charging for rides inside its two theme parks, Disneyland and Disney World
Which of the following statements regarding Disney's pricing strategy is true? A) At one time, customers had to pay for admission and rides at Disneyland and Disney World. Disney has since changed its pricing policy; it earns higher profits by charging for rides but not for admission. B) At one time, fees for admission and rides at both parks were set at their profit-maximizing levels. Disney has since changed its pricing policy; it uses a cost-plus pricing strategy for admission and does not charge for rides. C) At one time, customers had to pay for admission and rides at Disneyland and Disney World. Disney has since changed its pricing policy; it earns higher profits by charging for admission but not for rides. D) At one time, admission fees were charged at both parks but all rides were free. Disney has since changed its pricing policy; it earns higher profits by charging for both admission and rides.
A monopolistically competitive firm differs from a perfectly competitive firm in that a monopolistically competitive firm: a. faces a downward-sloping demand curve for its product
b. faces a horizontal demand curve at the market-clearing price. c. is able to earn profits in the long run. d. faces virtually no barriers to entry.
Why has the U.S. natural rate of unemployment fallen since the early 1990s?
What will be an ideal response?