The study of microeconomics and macroeconomics differ in that:
A. microeconomics is concerned with the domestic economy and macroeconomics is concerned only with the international economy.
B. microeconomics examines the individual markets of the economy while macroeconomics studies the whole economy.
C. microeconomics studies the actions of households and macroeconomics studies the actions of business firms.
D. microeconomics examines the whole economy while macroeconomics studies the individual units of the economy.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The formal definition of price elasticity of demand is
A) change in quantity demanded divided by change in price. B) quantity demanded divided by price. C) percentage change in quantity demanded divided by percentage change in price. D) quantity demanded multiplied by price and divided by 100.
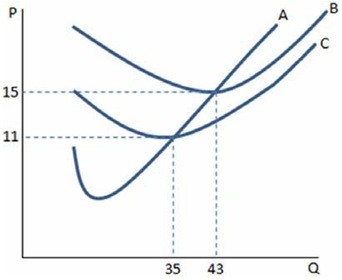 If a firm in a perfectly competitive market faces the cost curves in the graph shown, which of the following is true? The firm:
If a firm in a perfectly competitive market faces the cost curves in the graph shown, which of the following is true? The firm:
A. if it produces at profit-maximizing level of output it will make positive profits when price is higher than $11. B. will shut down if market price is below $15, but above $11. C. if it produces at profit-maximizing level of output it will make positive profits when price is higher than $15. D. should always produce at least 43 units in order to maximize profits.
If a firm increases all of its inputs by 10 percent and its output increases by 15 percent, then:
A. it is encountering economies of scale. B. the law of diminishing returns is taking hold. C. it is encountering diseconomies of scale. D. the firm's long-run ATC curve will be rising.
The unemployment rate in an economy is 7.5 percent. The total population of the economy is 250 million and the size of the civilian labor force is 180 million. The number of employed workers in this economy is:
A. 13.5 million B. 15.7 million C. 166.5 million D. 174.6 million