What is normal profit? How is it different from accounting profit?
If the difference between the total revenue of a firm and its implicit costs is equal to zero, the firm is said to be earning zero profit or a normal profit. Normal profit includes all the implicit costs as well as the explicit costs of production, while accounting profit includes only the explicit costs.
You might also like to view...
In the Friedman-Lucas money surprise model
A) If actual inflation is higher than anticipated inflation, then output must be above its trend value. B) If actual inflation is higher than anticipated inflation, then output must be below its trend value. C) money is neutral. D) monetary policy does not work.
When negative externalities exist, the private market equilibrium represents a
A) market price which is too low and a market quantity which is too low. B) market price which is too low and a market quantity which is too high. C) market price which is too high and a market quantity which is too low. D) market price which is too high and a market quantity which is too high.
Consider the following simple regression model y = 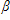
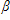
src="@@PLUGINFILE@@/ppg__cognero__Ch_15_Instrumental_Variables_Estimation_and_Two_Strage_Least_Squares__media__724969d3-56c7-4675-83d3-90a5aadf476f.PNG" style="vertical-align:-3px;" width="10px" height="19px" /> 0, the value of 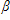
B.
C. Cov(z,u)
D. Cov(z,x)
In a decreasing-cost industry, an increase in industry output will
A) lead to a higher market price. B) lead to a lower market price. C) shift each firm's average fixed cost curve up. D) shift each firm's short run supply curve up.