Another toxin that also blocks neurotransmitter release is tetanus toxin; however, it primarily affects inhibitory interneurons of the spinal cord that negatively regulate motor neurons. Which would be symptoms of tetanus toxin poisoning?
A. flaccid paralysis
B. spastic paralysis
C. slowed action potential conduction
D. pupil dilation
Clarify Question
· What is the key concept addressed by the question?
· What type of thinking is required?
Gather Content/Choose Answer
· What do you already know about tetanus? What other information is related to the question?
Reflect on Process
· Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
B. spastic paralysis
Clarify Question
· What is the key concept addressed by the question?
o What are the effects of tetanus toxin?
· What type of thinking is required?
o This is an evaluate question because you need to take information about inhibitory neurons and motor neurons and predict clinical symptoms from a toxin that disrupts the communication between the two types of neurons.
Gather Content/Choose Answer
· What do you already know about tetanus? What other information is related to the question?
o To solve this problem, you’ll need to know that inhibitory interneurons of the spinal cord inhibit signals going to motor neurons that control skeletal muscles. If these interneurons are not functioning to regulate signals going to motor neurons, they would be firing all the time, producing continual muscle contraction (or spastic paralysis). This would not slow action potential conduction rate (answer C) but would increase the rate of action potentials going to motor neurons. Pupil dilation is controlled by the autonomic system in the brain and so is not affected by changes in the spinal cord.
Reflect on Process
· Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
o If you figured out the correct answer, great! If not, where did you go wrong? Did you confuse the definitions of flaccid and spastic paralysis? Did you think that inhibitory interneurons slow down action potential conduction of motor neurons? Remember that two negatives equal a positive, so if you inhibit an inhibitor, you end up with excitation, which is what happens to motor neurons when their inhibiting interneurons are stopped.
You might also like to view...
X inactivation can lead to ____________________ in females. Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s)
Balance is maintained by
A. the tympanum. B. ear bones. C. semicircular canals. D. the auditory tube.
The figure below shows five water molecules. The hydrogen bonds shown in this figure are each between
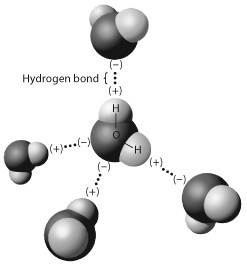
A) two hydrogen atoms.
B) an oxygen and a hydrogen atom of the same water molecule.
C) an oxygen and a hydrogen atom of different water molecules.
D) two atoms with the same charge.
Which does not describe eukaryotic flagella?
A) anchored by a basal body connected to a centriole B) whip-like motion C) 9+2 arrangement of microtubules D) plasma membrane-enclosed E) flagellin protein