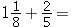 ________ (in proper form and reduced to lowest terms) If the answer results in a mixed number be sure to include a space between the whole number and the fraction. Example: 1 1/4 (read as one and one-fourth).
________ (in proper form and reduced to lowest terms) If the answer results in a mixed number be sure to include a space between the whole number and the fraction. Example: 1 1/4 (read as one and one-fourth).
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
1 21/40
The LCD is 40.![]()
You might also like to view...
A nursing aide has been given a formal written warning regarding arguing repeatedly on several occasions with the team leader about the given assignment. Today the nursing aide has taken four lengthy personal phone calls during her work time
This is the first offense of this nature. Such phone calls are prohibited in the employee handbook. The nurse manager calls the aide into the office and proceeds with which choice of action? A) Provide an explanation for the rule and proceed to give a verbal admonishment B) Ask whether there is a personal problem you could help solve C) Write up a formal reprimand D) Suspend the employee for a week
What instruction should the nurse provide to the client who is scheduled to have an abdo-minal ultrasound for evaluation of uterine size and shape?
A. "Do not eat or drink after midnight." B. "Completely evacuate your bowels before this procedure." C. "Do not urinate within an hour of having the test, because a full bladder is needed for best test results." D. "Have someone drive you to and from the test because you will be sleepy from the anesthesia."
For which complication does the nurse remain alert when a patient is taking any type of diuretic?
a. Loss of appetite b. Bladder spasms c. Hypertension d. Dehydration
The use of the terms health professional shortage areas (HPSAs), medically underserved areas (MUAs), and medically underserved populations (MUPs) is part of the system that establishes a designation that becomes the focus of federal assistance
What is a medically underserved area? A) Geographic area, population group, or medical facility with shortages of health care professionals that may not allow a full complement of health care services B) Determined with a calculation of a ratio of primary medical care physicians per 1,000 population, infant mortality rate, percentage of the population with incomes below the poverty level, and percentage of the population age 65 or older C) U.S. federal designation for those populations that face economic barriers (low-income or Medicaid-eligible populations) or cultural and/or linguistic access barriers to primary medical care services D) A subgroup of the population that has a higher risk of developing health problems because of a greater exposure to health risk because of marginalization