Using the HO model, assume that the United States is capital abundant and Mexico is labor abundant. If soybeans are capital intensive and avocados are labor intensive, it would be reasonable to expect the United States to
A) specialize completely in soybean production.
B) specialize completely in avocado production.
C) increase soybean production, but still produce some avocados.
D) increase avocado production, but still produce some soybeans.
C
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, a tax increase that decreases aggregate demand from AD1 to AD will lead to a short-run equilibrium at point ________ and eventually to a long-run equilibrium at point ________, if left to self-correcting tendencies.
A. D; C B. D; B C. A; B D. B; C
If producers incorrectly set the price of their product too low:
A. equilibrium will result. B. the industry will die out soon. C. a shortage will result. D. a surplus will result.
Writing in the New York Times on the technology boom of the late 1990s, Michael Lewis argues, "The sad truth, for investors, seems to be that most of the benefits of new technologies are passed right through to consumers free of charge." What does Lewis
means by the benefits of new technology being "passed right through to consumers free of charge"? A) Firms in perfect competition are price takers. Since they cannot influence price, they cannot dictate who benefits from new technologies, even if the benefits of new technology are being "passed right through to consumers free of charge." B) In perfect competition, price equals marginal cost of production. In this sense, consumers receive the new technology "free of charge." C) In the long run, price equals the lowest possible average cost of production. In this sense, consumers receive the new technology "free of charge." D) In perfect competition, consumers place a value on the good equal to its marginal cost of production and since they are willing to pay the marginal valuation of the good, they are essentially receiving the new technology "free of charge."
Refer to the graph, in which Dt is the transactions demand for money, Dm is the total demand for money, and Sm is the supply of money. If the interest rate was 4 percent, the asset demand for money would be:
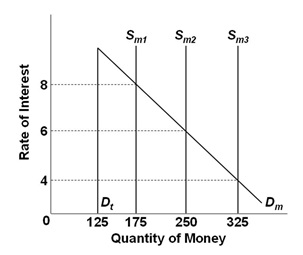
A. $125
B. $175
C. $200
D. $225