In a perfectly competitive market, if price is greater than average total cost at the level of output where marginal cost equals marginal revenue:
A. the firm must be in long-run equilibrium.
B. the firm is earning an economic profit greater than zero.
C. the firm is earning an economic profit less than zero.
D. We cannot determine whether the firm is earning positive or negative profits.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Classical economists believed that:
a. price flexibility automatically directs market economies to full employment. b. budget deficits and surpluses were necessary for the control of economic fluctuations. c. market economies suffer prolonged periods of recessions and depressions. d. market economies are inherently unstable because of fluctuating aggregate demand.
The most famous story about organizing tasks into jobs comes from Adam Smith's tale of the pin factory. In that story, he argues that
A. cross-training is critical for productivity. B. one worker should be assigned all the tasks in pin construction. C. coordination is the biggest problem for factory efficiency. D. specialization of jobs into simple tasks increases productivity.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 3.18 below to answer the question(s) that follow.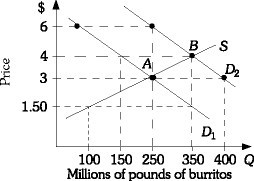 Figure 3.18Refer to Figure 3.18 The market is initially in equilibrium at Point A. If demand shifts from D1 to D2, the equilibrium price will change from ________ and the equilibrium quantity will change from ________.
Figure 3.18Refer to Figure 3.18 The market is initially in equilibrium at Point A. If demand shifts from D1 to D2, the equilibrium price will change from ________ and the equilibrium quantity will change from ________.
A. $3.00 to $4.00; 250 to 350 B. $4.00 to $3.00; 350 to 250 C. $4.00 to $3.00; 250 to 350 D. $3.00 to $4.00; 350 to 250
An increase in the equilibrium price for a product will result
A) when the quantity of the product demanded exceeds the quantity supplied. B) when there is a decrease in supply and an increase in demand for the product. C) when there is a decrease in supply and a decrease in demand for the product. D) when there is an increase in demand and an increase in the number of firms producing the product.