At what temperature would the root-mean-square speed of hydrogen, H2, molecules equal 11.2 km/s (the earth's escape speed)? The mass of a hydrogen atom is 1.67 × 10-27 kg, and the Boltzmann constant is 1.38 × 10-23 J/K
A) 1.01 × 102 K
B) 1.01 × 104 K
C) 1.01 × 106 K
D) 1.01 × 108 K
B
You might also like to view...
Degeneracy pressure is the source of the pressure that stops the crush of gravity in all the following except
A) a brown dwarf. B) a white dwarf. C) a neutron star. D) a very massive main-sequence star. E) the central core of the Sun after hydrogen fusion ceases but before helium fusion begins.
The Bohr model pictures a hydrogen atom in its ground state as a proton and an electron separated by the distance a0 = 0.529 × 10?10 m. The electric potential created by the proton at the position of the electron is
A. ?13.6 V. B. +13.6 V. C. ?27.2 V. D. +27.2 V. E. +5.12 × 109 V.
When dark matter is added, what happens to the speeds of the inner and outer stars?
A.) All the speeds increased the same. B.) The stars near the center slowed down, but the outer ones were accelerated. C.) All the stars sped up, but the outer ones gained the most speed. D.) All were slowed down by the tidal drag of the dark matter. E.) There was no change.
Answer the following statement(s) true (T) or false (F)
1. A particle’s Newtonian x-momentum 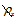 is always either equal to or smaller than the x component of the particle’s four-momentum px
is always either equal to or smaller than the x component of the particle’s four-momentum px
2. A particle’s mass is always either equal to or smaller than the time-component of its four-momentum
3. The absolute value of the x component of a particle’s four-momentum vector is always either equal to or smaller than its t component
4. The squared magnitude of a four-vector could be negative.
5. The squared magnitude of a particle’s four-momentum could be negative.