What are the four main sources of comparative advantage? Briefly explain each source and provide examples
What will be an ideal response?
The 4 main sources cited are:
1. climate and natural resources
2. relatively abundant supplies of labor and capital
3. technology
4. external economies.
Some examples of natural-resource-rich countries include Saudi Arabia (rich in oil), Malaysia (rich in palm oil), Indonesia (rich in tropical hardwoods), and Kenya with its exotic wildlife (for tourism). Advantageous climate is also a source of comparative advantage. For example, the South of France and certain parts of Italy have a particular blend of climatic conditions and land that is well suited to the cultivation of truffles.
Countries like the United States have many highly-skilled workers and a huge stock of capital equipment compared to, say, China and India which have more low-skilled workers and relatively little machinery. As a result, the United States has a comparative advantage in the production of goods that require skilled workers or sophisticated machinery (software, biotechnology) while China and India have a comparative advantage in the production of goods that require low-skilled workers and small amounts of simple machinery (carpets, clothing items).
The text discusses the distinction between product technologies and process technologies and how they lead to specialization in different kinds of products. For example, the United States is undoubtedly the world leader in research and development leading to a comparative advantage in technology-intensive products and services. Examples include the development of new products in the fields of medicine, telecommunications, and bioengineering. Countries that are strong in process technologies are likely to concentrate on improving the process used to make existing products.
External economies occur outside of a firm, within an industry. Thus, when an industry's scope of operations expands due to, for example, the creation of a better transportation network, firms located in that network gain advantages over firms located outside the network.
You might also like to view...
Given the information in Scenario 4.3, erasers and good b, are:
A) substitutes. B) complements. C) completely unrelated. D) normal. E) inferior.
Average cost is the cost of producing the next unit
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Straker Industries estimated its short-run costs using a U-shaped average variable cost function of the formAVC = a + bQ + cQ2and obtained the following results. Total fixed cost (TFC) at Straker Industries is $1,000. 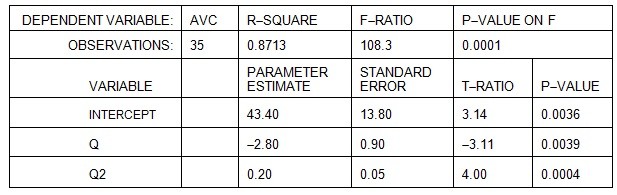 If Straker Industries produces 20 units of output, what is estimated total variable cost (TVC)?
If Straker Industries produces 20 units of output, what is estimated total variable cost (TVC)?
A. $2,348 B. $1,498 C. $1,348 D. $4,428
The perfect competitor's demand and marginal revenue curves ______ identical; the monopolist's demand and marginal revenue curves _______ identical.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).