All firms in a competitive industry have the following long-run total cost curve:
C(q) = q3 – 10q2 + 36q
where q is the output of the firm.
a. Compute the long run equilibrium price. What does the long-run supply curve look like if this is a constant cost industry? Explain.
b. Suppose the market demand is given by Q = 111 – p. Determine the long-run equilibrium number of firms in the industry.
a. Long run equilibrium is determined by (1 ) the minimum of the AC curves, and (2 ) the demand equation.
The AC is at a minimum where AC = MC:
Q = 5, AC = MC = 11
Therefore, the long run price will be $11 and each firm will produce 5 units.
b. The market quantity (from demand) is 100 and so 20 firms will exist in this market. The long run supply curve is flat at $11 because the price will always equal this due to free entry and exit of firms.
You might also like to view...
Stocks and bonds issued in banking-oriented systems are rather __________ because they are traded __________
A) liquid; frequently B) liquid; infrequently if at all C) illiquid; frequently D) illiquid; infrequently if at all
List two economic reasons why representative democracy makes sense
What will be an ideal response?
According to the graph shown, if the economy were to open to free trade, it would become:
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good, as well as a tariff and the world price for that good.
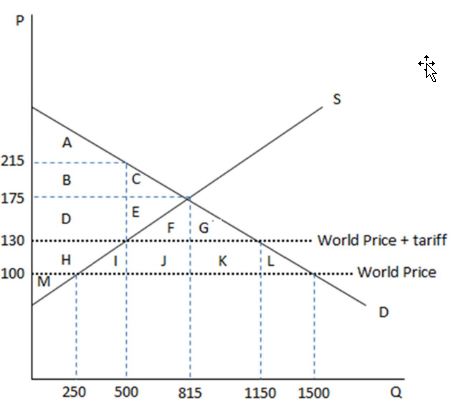
A. a net-importer.
B. a net-exporter.
C. an autarky.
D. less efficient with less overall market surplus.
Which of the following is an argument against balancing the federal budget?
A. Doing so may prevent the government from pulling the economy out of recession. B. An increase in government spending and taxes by the same amount does not affect income. C. The economy will self-adjust so deficit spending is not necessary. D. None of the choices are correct.