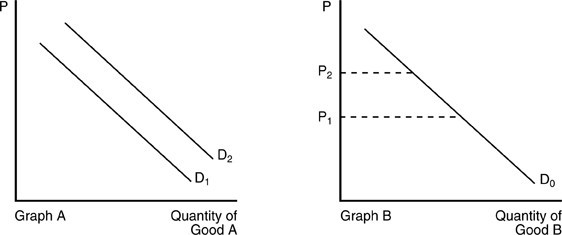
 In the above figure, the demand curve for Good A shifts from D1 to D2 in Graph A when the price of Good B changes from P1 to P2 in Graph B. We can conclude that
In the above figure, the demand curve for Good A shifts from D1 to D2 in Graph A when the price of Good B changes from P1 to P2 in Graph B. We can conclude that
A. Good A and Good B are complements.
B. Good A and Good B are unrelated.
C. Good A and Good B are substitutes.
D. Good A is a normal good but Good B is an inferior good.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is classified as an intermediate good?
i. the purchase of a Big Mac by a college student ii. McDonald's purchase of pickles iii. a McDonald's restaurant owner's interest payment for the loan on her building A) ii only B) ii and iii C) i and iii D) i only E) i, ii and iii
Which of the following is NOT an implication of the theory of purchasing power parity?
A) Exchange rates move to equalize the purchasing power of different currencies. B) Exchange rates should be at a level that makes it possible to buy the same amount of goods and services with the equivalent amount of any country's currency in the long run. C) A country with a higher inflation rate should experience an appreciation of its currency. D) The real exchange rate should equal one.
The marginal product generated by an additional unit of input times the price of the output is called:
A. the marginal revenue product. B. the value of the marginal product. C. Both of these statements are true. D. Neither of these statements is true.
A separate legal entity established by two or more companies to pursue shared business objectives.
What will be an ideal response?