The price/earnings (PE) ratio of a stock is found by
a. dividing the most recent year's dividend by the current stock price
b. dividing the current stock price by the after-tax profit per share
c. dividing the most recent year's dividend by retained earnings
d. dividing the current stock price by the Dow Jones Industrial Average
e. dividing the current stock price by the present value of the firm
B
You might also like to view...
A broad and liquid market means that
a. stock markets list a large number of shares. b. owners can sell stock but only at a discount. c. shareholders can sell at any time at the market price d. insider trading laws are observed. e. none of the above.
A representative sample
A. eliminates the problem of response bias. B. is frequently a random sample. C. reflects the characteristics of the population. D. both b and c E. all of the above
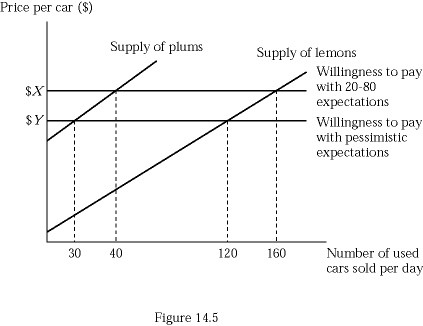 Figure 14.5 represents the market for used cars. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $5,000 for a plum (high-quality) used car and $3,000 for a lemon (low-quality) used car. If buyers believe that 80% of used cars in the market are lemons (low quality), what percent of used cars sold will actually be plums?
Figure 14.5 represents the market for used cars. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $5,000 for a plum (high-quality) used car and $3,000 for a lemon (low-quality) used car. If buyers believe that 80% of used cars in the market are lemons (low quality), what percent of used cars sold will actually be plums?
A. 20% B. 25% C. 33.33% D. 75%
An agribusiness firm may undertake three alternatives: buy cane sugar and manufacture various sugars and sweets, making a profit of $12 million; buy corn and produce ethanol, making a profit of $16 million; or buy wheat and produce breads, rolls, and
pastries, making a profit of $13 million. The opportunity cost associated with these three choices is A) $4 million. B) $3 million. C) $13 million. D) $16 million.