Which statement is true about the graph above?
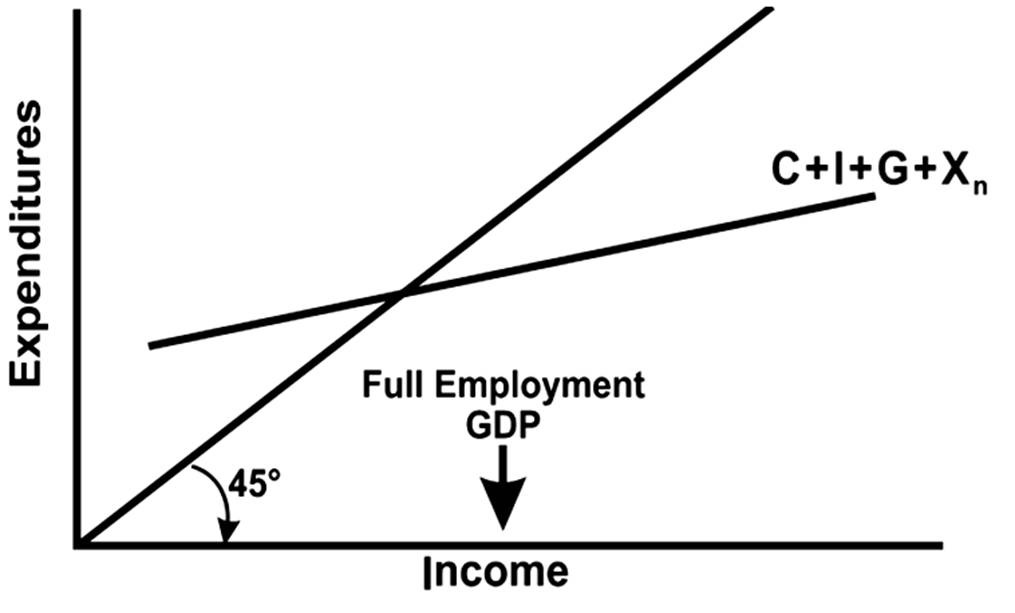
A. Equilibrium GDP is too big.
B. Equilibrium GDP is too small.
C. Equilibrium GDP is just the right size.
D. There is not enough information to determine whether or not equilibrium GDP is the right size.
B. Equilibrium GDP is too small.
You might also like to view...
Assume thatthe market demand for organic tomatoesis modeled as QD= 104 – 2P and market supply is QS = 20 + 4P. If the actual price is set at $20 per pound, there is a _________ of _______ units of the good.
a. surplus; 36 c. shortage; 10 b. surplus; 26 d. none of the above
The average level of tariffs on imported products charged by industrialized countries changed between 1946 and 1990
a. from 5 percent to 40 percent. b. from 40 percent to 5 percent. c. from 10 percent to 20 percent. d. from 20 percent to 10 percent.
Which of the following will always be true when an economy is in long-run equilibrium?
a. The level of prices will be constant (that is, inflation will be zero). b. Actual output will exceed the potential output. c. The actual rate of unemployment will be less than the natural rate of unemployment. d. The output of the economy will correspond with the full-employment output.
The principle of comparative advantage does not provide answers to certain questions. One of those questions is
a. Do specialization and trade benefit more than one party to a trade? b. Is it absolute advantage or comparative advantage that really matters? c. How are the gains from trade shared among the parties to a trade? d. Is it possible for specialization and trade to increase total output of traded goods?