A hollow conducting spherical shell of radius 1.20 cm carries a charge of -5.20 nC. What is the electric field at a distance of 1.50 cm from the center of the shell?
A. 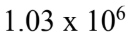
B. 0 N/C
C. 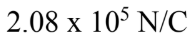
D. 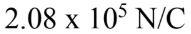
E. 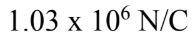
C. 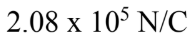
You might also like to view...
Why do we sometimes observe asteroids at the distances of the gaps in the asteroid belt?
A) Jupiter's gravitational tugs keep them there.
B) They are held in place by resonances with other asteroids.
C) Actually, we never see asteroids in the gaps.
D) They are kept in place by shepherding asteroids.
E) A gap is located at an average orbital distance, and asteroid orbits often have large eccentricities.
An ice cube is floating in a glass of water with the water level just reaching the top of the glass. If the temperature in the surrounding area is above freezing, the ice cube will melt. When it does,
A. the water level in the glass will remain unchanged as the ice continues to melt. B. the water level in the glass will begin to go down. C. water will begin to spill over the top of the glass. D. it is impossible to tell what the water level will do from the information given.
Consider a 2.4 kilogram feather (Big Bird) on the planet Mars. [Earth mass = 6.0 × 1024 kg = 9.3 × Mars mass; Earth radius = 6380. km = 1.89 × Mars radius]
(a) What does the feather weigh on Mars? (b) What would the same feather weigh on Earth?
Two concentric imaginary spherical surfaces of radius R and 2R, respectively, surround a positive point charge Q located at the center of the surfaces. When compared to the electric flux ?1 through the surface of radius R, the electric flux ?2 through the surface of radius 2R is
A.
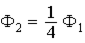 .
.B.
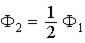 .
.C.
D.
E.