The combined effect (both income and substitution) of a wage increase is that
A) if the substitution effect outweighs the income effect, the labor supply curve slopes upward, but if the income effect outweighs the substitution effect, the labor supply curve is backward bending.
B) the income effect always dominates, leading to less work at a higher wage.
C) if the substitution effect outweighs the income effect, the labor supply curve is backward bending, but if the income effect outweighs the substitution effect, the labor supply curve slopes upward.
D) the substitution effect always dominates, leading to more work at a higher wage.
A
You might also like to view...
The practice of setting price by increasing the average costs of production by some percentage is referred to as:
A) average cost pricing. B) percentage pricing. C) rate-of-return pricing. D) markup pricing.
In a competitive industry buffeted by demand and supply shocks, prices increase and decrease, but economic profits tend to revert to zero. Hence, profits are exhibiting
a. Above-average return b. Positive earnings c. Mean reversion d. None of the above
The accompanying figure shows the demand curve for a product that can be sold only in whole-number amounts.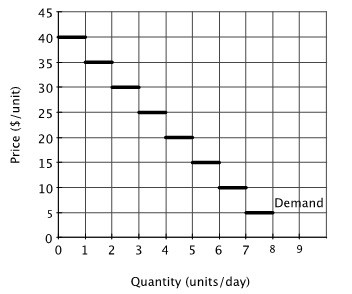 At a price of $15 per unit, what would be the total consumer surplus in this market each day?
At a price of $15 per unit, what would be the total consumer surplus in this market each day?
A. $75 B. $0 C. $6 D. $15
Based on this figure, if the krone exchange rate is fixed at $0.09 dollars per krone, the krone is: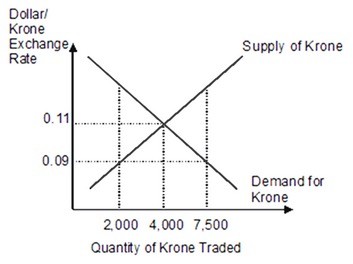
A. devalued. B. undervalued. C. revalued. D. overvalued.