Use the following figure showing the domestic demand and supply curves for product B in a hypothetical economy to answer the next question.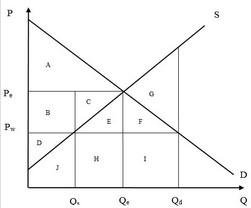 After trade, at a world price of Pw, producer surplus equals area(s)
After trade, at a world price of Pw, producer surplus equals area(s)
A. E + H + J.
B. B + C.
C. D.
D. B + C + D.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Total planned expenditure (equals income) is 13,500, autonomous consumption expenditure is 600, the marginal propensity to consume is 0.8, government purchases are 2,700, taxes are 2,500 and planned investment spending is 2,900
Net exports is ________. A) 3,840 B) negative 1,500 C) negative 1,380 D) negative 1,340 E) 2,100
According to the monetarist view, the
a. IS schedule is quite flat; hence, reflecting a high interest elasticity of aggregate demand. b. IS schedule is quite steep; hence, reflecting a high interest elasticity of aggregate demand. c. LM schedule is quite flat; hence, reflecting a high interest elasticity of money demand. d. IS schedule is almost vertical; hence, reflecting a very low interest elasticity of money demand.
The difference between the marginal expenditure and the wage is greater when the supply curve of labor is
A) less elastic at the monopsony optimum. B) more elastic at the monopsony optimum. C) more elastic than the demand curve. D) The difference does not depend on any elasticity.
If price elasticity of supply is less than 1
A) supply is elastic. B) demand is elastic. C) demand is inelastic. D) supply is inelastic.