The local mall has a make-your-own sundae shop. They charge customers 35 cents for each fresh fruit topping and 25 cents for each processed topping. Barbara is going to make herself a sundae
The total utility that she receives from each quantity of topping is given by the following table: Fresh Fruit Topping Processed Topping # of Units Total Utility # of Units Total Utility 1 10 1 10 2 18 2 20 3 24 3 10 4 28 4 0 5 30 5 -10 6 28 6 -20 7 24 7 -30 8 18 8 -40 9 10 9 -50 10 -6 10 -60 a. What is the marginal utility of the 6th fresh fruit topping? b. Of the two toppings, which would Barbara purchase first? Explain. c. If Barbara has $1.55 to spend on her sundae, how many fresh fruit toppings and processed toppings will she purchase to maximize utility? d. If money is no object, how many fresh fruit toppings and processed toppings will Barbara purchase to maximize utility? e. Which of the basic assumptions of preferences are violated by preferences shown in the table above?
a. The marginal utility of the 6th fresh fruit topping is -2 utils (28 utils - 30 utils).
b. Barbara will purchase the topping that provides the largest marginal utility per dollar spent. The marginal utility divided by price for the first unit of fresh fruit topping is 10/.35. The marginal utility divided by price for the first unit of processed topping is 10/.25. Thus the first topping purchased will be processed (because 10/.25 > 10/.35).
c. Barbara will continue to purchase toppings, one at a time, until she spends $1.55, by always selecting the topping that provides the largest marginal utility per dollar spent. Barbara will purchase 2 processed toppings first, followed by 3 fresh fruit toppings.
d. If money is no object, Barbara will purchase an additional unit of each topping as long as the topping provides a positive marginal utility. In this case, 2 processed toppings and 5 fresh fruit toppings.
e. The preferences used in this problem violate the assumption that consumers always prefer more of a good to less.
You might also like to view...
The United States generally has a comparative advantage in the development of technology because it has:
A. large amounts of natural resources. B. patent laws, which no other country has. C. a disproportionate share of the world's best research universities. D. the greatest need for new technology.
The definition of gross domestic product is
A. the total value of all sales in the economy. B. the total value of production in the domestic economy plus the production of domestic firms in foreign countries. C. the total value of all sales of final and intermediate goods in the domestic economy. D. the total of the money values of all final goods and services produced in the domestic economy within a specific time period.
An inverted yield curve is a valuable forecasting tool because:
A. investors are expecting higher short-term rates in the future, and this usually signals an economic slowdown. B. inverted yield curves signal better economic times are expected. C. the yield curve usually is inverted so it reflects a growing economy. D. the yield curve seldom is inverted and can signal an economic slowdown.
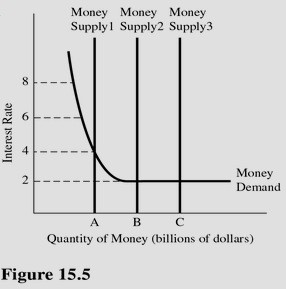 According to Figure 15.5, the liquidity trap occurs at an interest rate of
According to Figure 15.5, the liquidity trap occurs at an interest rate of
A. 8 percent only. B. 2 percent, 4 percent, 6 percent, and 8 percent. C. 2 percent and 4 percent. D. 2 percent only.