The labor demand curve of an imperfectly competitive seller is downsloping:
A. solely because of diminishing marginal utility.
B. because of both diminishing returns and the necessity to lower price to sell more output.
C. solely because product price must be reduced to sell more output.
D. solely because of diminishing returns.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The economy pictured in the figure has a(n) ________ gap with a short-run equilibrium combination of inflation and output indicated by point ________. 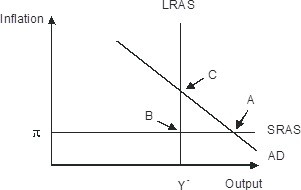
A. recessionary; A B. recessionary; C C. recessionary; B D. expansionary; A
In perfect competition, each additional unit of output that a firm sells will yield a marginal revenue that is
A. less than price. B. equal to price. C. equal to average total cost. D. greater than price.
To join the EMU, a country must have
A) a public-sector deficit no higher than 3 percent of its GDP in general. B) a public-sector deficit no higher than 2 percent of its GDP in general. C) a public-sector deficit no higher than 1 percent of its GDP in general. D) a zero public-sector deficit. E) a public-sector deficit no higher than 4 percent of its GDP in general.
Supply-side economics focuses on how fiscal policy might be used to
A. increase consumption. B. increase aggregate supply. C. increase aggregate demand to the full-employment level of real GDP. D. align aggregate demand and aggregate supply.