Briefly explain diffraction fringes
What will be an ideal response?
One consequence of the wavelike nature of light is that there is an inevitable small blurring called a diffraction fringe around every point of light in the image, and you cannot see any detail smaller than the fringe. Astronomers can't eliminate diffraction fringes, but the fringes are smaller in larger telescopes, and that means they have better resolving power and can reveal finer detail.
You might also like to view...
Graphical Analysis: The graph in the figure shows the position of a particle as it travels along the x-axis. What is the magnitude of the average speed of the particle between t = 1.0 s and t = 4.0 s?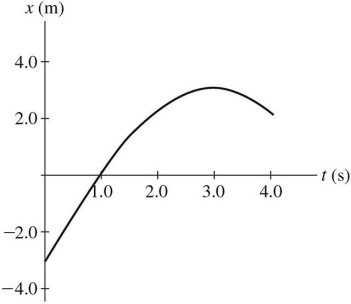
A. 1.0 m/s B. 1.3 m/s C. 0.67 m/s D. 0.50 m/s E. 0.25 m/s
Which of the following states is not possible for n = 4?
1.4h 2.4f 3.4d 4.4s
The frequency of blue light is ________ that of green light.
A. less than B. greater than C. the same as D. greater than, the same as, or less than, depending on a source of light
Air is flowing straight toward a building. What expression would provide ?p/?x if x is measured perpendicular to the building? Neglect viscous and gravity effects and assume steady flow.
(A) ?p/?x = ?? (u?u/?x ? v?v/?y) (B) ?p/?x = ?? u?u/?x (C) ?p/?x = ?? v?u/?x (D) ?p/?x = ?? (u?u/?x ? v?u/?y)