Consumers' surplus is the difference between the price
A) sellers receive for a good and the maximum price they would have paid for the good.
B) sellers receive for a good and the minimum price for which they could have sold the good.
C) buyers pay for a good and the maximum price they would have paid for the good.
D) buyers pay for a good and the minimum price for which they would have sold the good.
C
You might also like to view...
The Prisoners' Dilemma is so named because
a. the Nash equilibrium is one of the worst outcomes for the players. b. the game has no Nash equilibrium. c. the game is zero-sum. d. players end up earning a lighter sentence than the prosecutor would like.
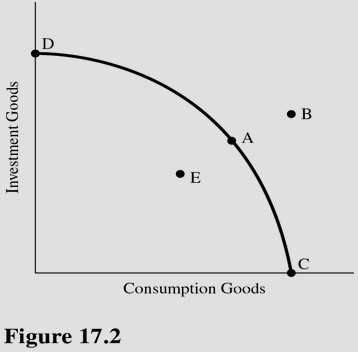 Refer to Figure 17.2. Ceteris paribus, if the economy produces at point C, which of the following is most likely?
Refer to Figure 17.2. Ceteris paribus, if the economy produces at point C, which of the following is most likely?
A. The PPC will not shift in the future. B. The PPC will shift outward in the future. C. The economy will continue to have point C as a choice in the future. D. The PPC will shift inward in the future.
The fact that output gaps will not last indefinitely, but will be closed by rising or falling inflation is the economy's:
A. income-expenditure multiplier. B. self-correcting property. C. short-run equilibrium property. D. long-run equilibrium property.
Suppose the economy currently has some underutilized resources. The Fed engages in expansionary monetary policy. The impact of expansionary monetary policy will be to
A. increase short-run aggregate supply, decrease prices and increase real GDP. B. increase aggregate demand, increase prices and increase real GDP. C. increase short-run aggregate supply, decrease in prices and decrease in real GDP. D. increase aggregate demand, increase prices and decrease real GDP.