In the figure below, the economy is initially in long-run equilibrium at point A. If there is an adverse supply shock that reduces potential output and shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve from LRAS to LRAS', then the new long-run equilibrium is reached at point: 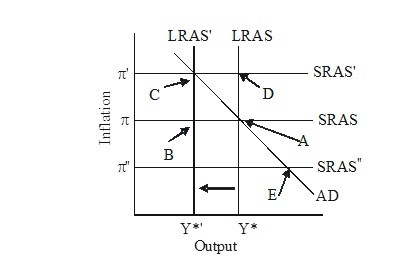
A. C.
B. D.
C. E.
D. B
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Suppose the required reserve ratio is 8% and that banks hold no excess reserves and the public does not change its currency holdings. If the Fed sells $5 million worth of securities, what happens to the amount of deposits in the banking system?
What will be an ideal response?
Suppose that a long-run adjustment in a perfectly competitive industry results in decreased industry output but leaves price unchanged. Which of the following must be true?
a. The market demand curve did not shift b. The market demand curve shifted left; the market supply curve shifted right c. The market supply curve shifted left; the market demand curve shifted right d. Both market supply and demand increased, but supply increased more than demand e. The industry is a constant-cost industry
An artificially scarce good is:
A. rival in consumption and excludable. B. not rival in consumption, but excludable. C. rival in consumption, but not excludable. D. not rival in consumption and not excludable.
A firm selling a good which lacks any good substitutes is called a(n)
a. pure monopoly. b. price discriminator. c. exclusive monopoly. d. natural monopoly.