Using the figure below, identify the labeled part.
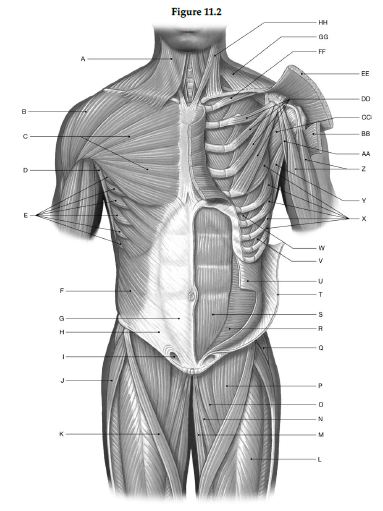
1) Label A: ______________________________
2) Label B: ______________________________
3) Label C: ______________________________
4) Label D: ______________________________
5) Label E: ______________________________
6) Label F: ______________________________
7) Label G: ______________________________
8) Label H: ______________________________
9) Label I: ______________________________
10) Label J: ______________________________
11) Label K: ______________________________
12) Label L: ______________________________
13) Label M: ______________________________
14) Label N: ______________________________
15) Label O: ______________________________
16) Label P: ______________________________
17) Label Q: ______________________________
18) Label R: ______________________________
19) Label S: ______________________________
20) Label T: ______________________________
21) Label U: ______________________________
22) Label V: ______________________________
23) Label W: ______________________________
24) Label X: ______________________________
25) Label Y: ______________________________
26) Label Z: ______________________________
27) Label AA: ______________________________
28) Label BB: ______________________________
29) Label CC: ______________________________
30) Label DD: ______________________________
31) Label EE: ______________________________
32) Label FF: ______________________________
33) Label GG: ______________________________
34) Label HH: ______________________________
1) Platysma
2) Deltoid
3) Pectoralis major
4) Latissimus dorsi
5) Serratus anterior
6) External oblique
7) Rectus sheath
8) Aponeurosis of external oblique
9) Superficial inguinal ring
10) Tensor fasciae latae
11) Sartorius
12) Rectus femoris
13) Gracilis
14) Adductor longus
15) Pectineus
16) Iliopsoas
17) Gluteus medius
18) Transversus abdominis
19) Rectus abdominis
20) External oblique (cut and reflected
21) Internal oblique (cut
22) External intercostal
23) Internal intercostal
24) Serratus anterior
25) Teres major
26) Biceps brachii (short and long heads
27) Coracobrachialis
28) Pectoralis major (cut and reflected
29) Subscapularis
30) Pectoralis minor
31) Deltoid (cut and reflected
32) Subclavius
33) Trapezius
34) Sternocleidomastoid
You might also like to view...
Which type(s) of subatomic particles can be located within the nucleus of an atom?
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following epithelial types is mismatched with its function?
A. Stratified epithelium - protection B. Simple epithelium - diffusion C. Squamous epithelium - stretching D. Cuboidal epithelium - absorption E. Columnar epithelium - secretion
The final equilibrium state reached by a molecule that enters a cell by facilitated diffusion is the same as that for a molecule that enters the cell by diffusion
Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
The type of membrane that protects internal organs from friction is a ________ membrane
A. dry B. serous C. synovial D. partial E. mucous