In perfect competition, one result of the model was that there were no economic profits in the long run. In a monopoly, the firm typically earns a positive economic profit. Why is there this difference?
The monopolist enjoys economic profit because of barriers to entry. In perfect competition, if there are economic profits, other firms will enter the industry, expand industry supply, and drive down the price and profit level until there are no economic profits. In a monopoly, although there are economic profits, entry does not occur because of barriers; therefore, the successful monopolist can enjoy economic profits in the long run.
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, an increase in government spending that increases aggregate demand from AD to AD1 will lead to a short-run equilibrium at point ________ creating _____gap. 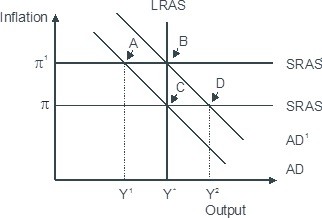
A. D; an expansionary B. B; no output C. B; expansionary D. A; a recessionary
If real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is $6 trillion, then unplanned business inventories will
A) rise. B) be zero. C) fall. D) be equal to planned inventories.
Suppose that when price is $10, quantity supplied is 20 . When price is $6, quantity supplied is 12 units. The price elasticity of supply is:
a. 0.5. b. 0.8. c. 1.0. d. 1.5. e. 2.0.
Which of the following is true about the equation of exchange??
a) The equation of exchange can be presented as: M + V = P + Q. b) Velocity represents the average number of times that a dollar is used in purchasing final goods or services in a one-year period. c) ?If M decreases, and V increases, then P must rise and/or Q must rise. d) All of the above are true about the equation of exchange.