What nucleotide change is a shared derived character for species A, B, and C, but not for species G?
Note: A,T,G, and C refer to nucleotide bases, and the numbers refer to the position of the base in the nucleotide sequences. For example, A6 refers to an adenine at the sixth position.
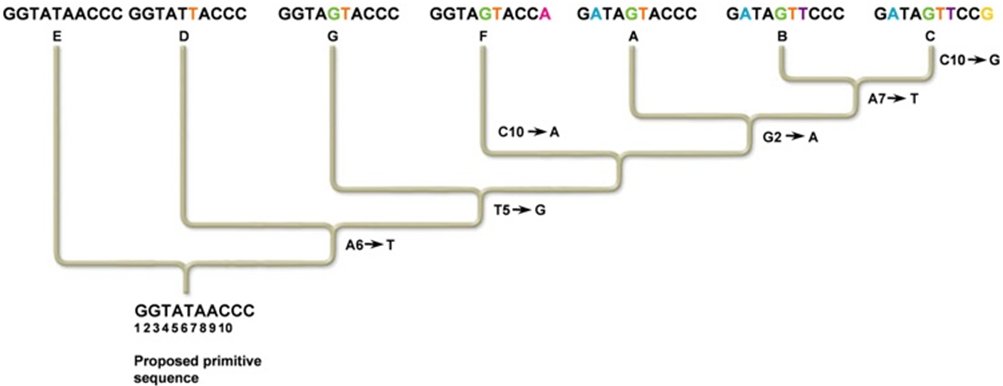
A. Changing the second G to an A is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G.
B. Changing the fifth T to a G is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G.
C. Changing the second G to a T is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G.
D. Changing the second G to an A and the fifth T to a G is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G.
E. None of these show a change in derived characteristics for A, B, and C that are not found in G.
A. Changing the second G to an A is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G.
You might also like to view...
According to a 2003 study performed by Michelle Khan and her coworkers, the rate of cervical cancer appears to be
the greatest when women are ____.
a. positive for HPV 16 b. negative for HPV16 but positive for HPV18 c. negative for HPV16/18 but positive for other cancer-causing HPV d. negative for all cancer-causing HPV e. positive for HIV
How is the net primary productivity of an ecosystem calculated?
What will be an ideal response?
How many unique haploid gametic genotypes could be produced through independent assortment by an organism with the diploid genotype AABbCCDdEe?
What will be an ideal response?
Which group of microbes prefers using oxygen but can survive without it?
A) aerotolerant anaerobe B) obligate aerobe C) facultative anaerobe D) obligate anaerobe E) microaerophile