When you compare Australian marsupials to placental mammals today
Marsupials are a very ancestral form of mammal, evolving before placental mammals over 70 million years ago. Today Australian marsupials can be compared to placental mammals on other continents.
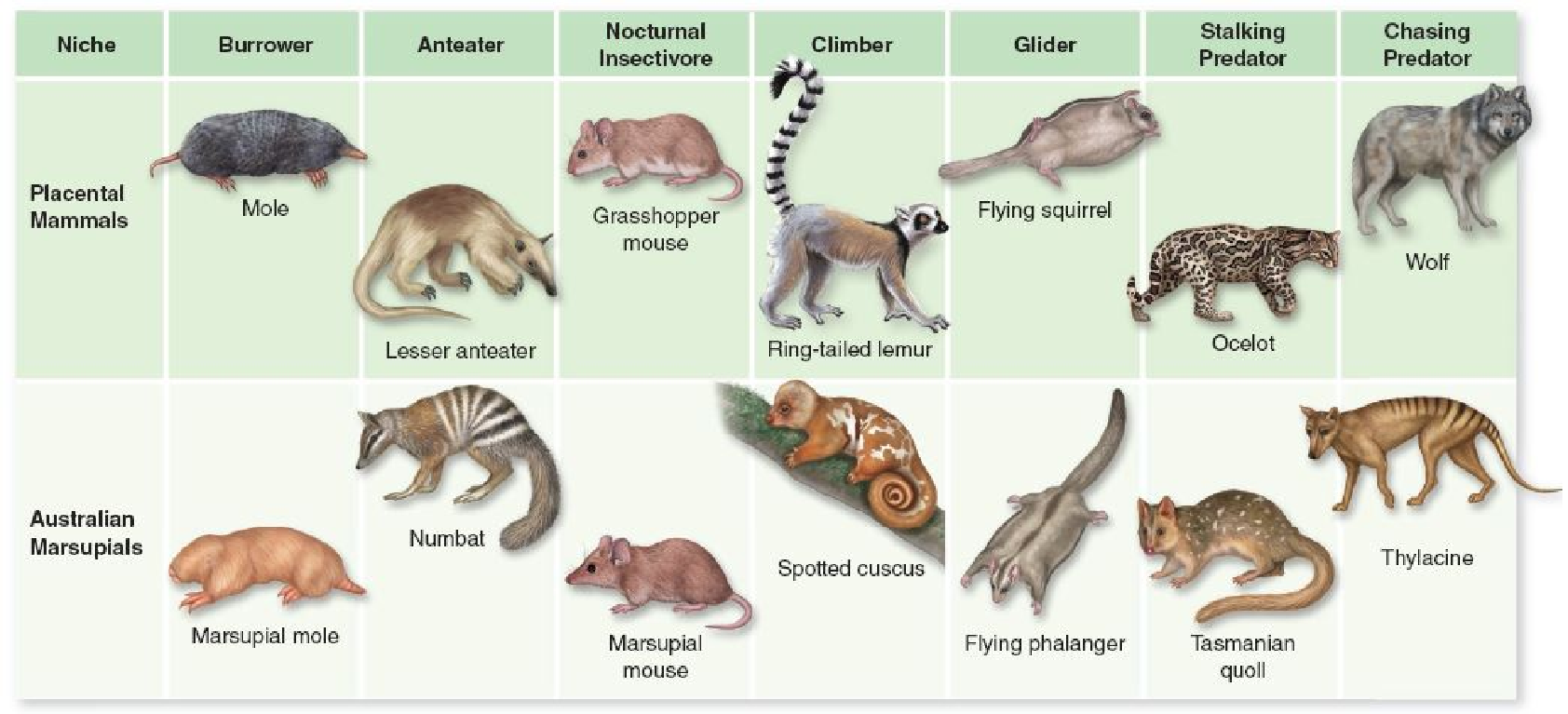
A. the marsupials are all very primitive, having changed very little during the last 70 million years.
B. the marsupials are very similar to placental mammals in the ways they have adapted to similar ecological niches.
C. the marsupials have evolved much more rapidly than placental mammals and are more highly adapted.
D. the marsupial fossils look remarkably similar to the placental mammals of today.
E. living marsupials are little changed from the earliest marsupial fossil forms.
B. the marsupials are very similar to placental mammals in the ways they have adapted to similar ecological niches.
You might also like to view...
The molecule shown above is testosterone, a substance that has important regulatory functions in
humans and many other animals. Molecules with regulatory functions like testosterone are called ____.
a. phytosterols b. enzymes c. lipoproteins d. hormones e. receptors
The function of the human stomach is
A. storage of food and mixing with digestive fluids to continue chemical digestion. B. to produce highly basic fluids to kill most bacteria. C. promotion of bacterial fermentation. D. to begin the absorption of most small food molecules, especially sugars and alcohol. E. absorption of iron to build hemoglobin for red blood cells.
These are a special group of toxins that activate T cells. This nonspecific means of activating T cells can trigger life-threatening autoimmune-like responses by stimulating the release of large amounts of interleukins, such as IL-1 and IL-2
A. endotoxins B. exotoxins C. superantigens D. supertoxins E. holotoxins (A-B toxins)
________ are toxic proteins secreted by pathogenic bacteria, and ________ are toxic components of the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria
A) Endotoxins; parasites B) Endotoxins; botulinum toxins C) Exotoxins; enterotoxins D) Exotoxins; endotoxins