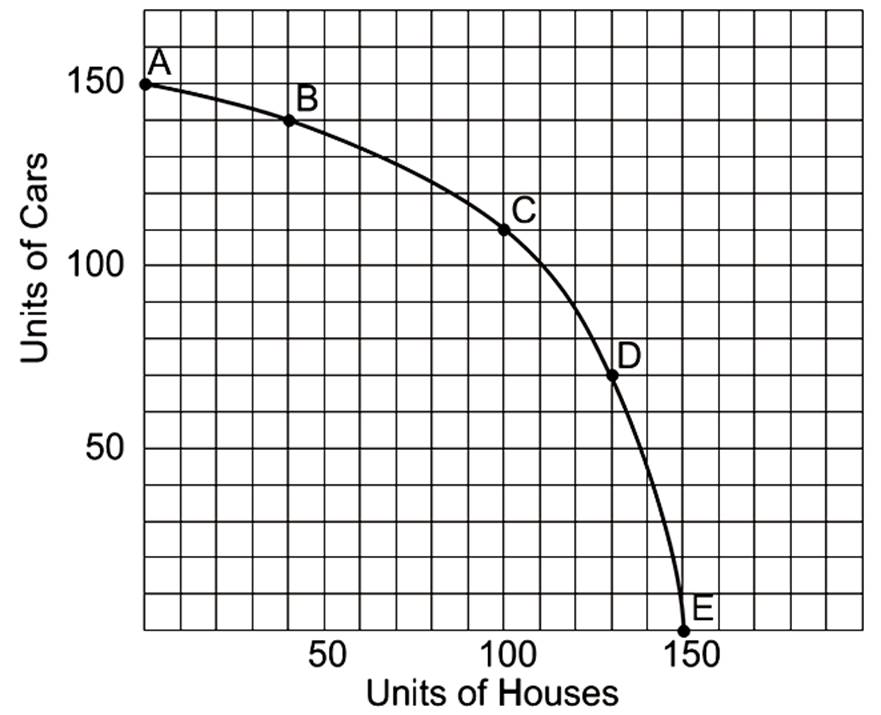
What is the opportunity cost of going from point D to point C?
10 CAT scans
You might also like to view...
According to the Keynesian model, the short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve is horizontal when
A) prices react to an aggregate demand shock but real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) does not. B) there are no unemployed resources and wages do not change when prices change. C) there are unemployed resources and prices do not fall when aggregate demand falls. D) real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is at full capacity but prices are not flexible.
In general, the more equitable the incidence of a tax system is the:
A. less complicated and more efficient is its design B. more complicated and less efficient is its design. C. more complicated and more efficient is its design. D. less complicated and less efficient is its design.
Which of the following statements is true?
A. Firms are unlikely to relocate their high-pollution production to countries with lax environmental laws because they fear that such moves will result in adverse effects on their reputations. B. Evidence shows that measures to keep the environment clean represent a large percentage of the total costs of production for a firm in a country with strict environmental laws. C. There are large incentives for firms to relocate from countries with strict environmental laws to countries with lax environmental regulation. D. Imposition of a tax on the production of a particular high-pollution product typically has a greater impact on consumer surplus than on producer surplus.
Goods that are produced in other countries and then sold domestically are called
A. quotas. B. exports. C. tariffs. D. imports.