Outline the equilibrium theory of tides, including its assumptions. What will be an ideal response?
The equilibrium theory of tides explains many characteristics of ocean tides by examining the
balance and effects of the forces that allow a planet to stay in a stable orbit around the sun, or
the moon to orbit Earth. The equilibrium theory assumes that the seafloor does not influence
the tides and that the ocean conforms instantly to the forces that affect the position of its surface; the ocean surface is presumed always to be in equilibrium (balance) with the forces
acting on it.
You might also like to view...
One sign of the environmental mismanagement of Russia's Lake Baikal in Siberia—the world's deepest and largest (by volume) lake—was the 1997 death of thousands of
A) Siberian black bears. B) migratory cranes. C) tourists from western Russia. D) freshwater seals E) the world's largest salmon.
If you began a trip at 60° west, 20° north and traveled 120° farther west and 50° south, your new position would be
A) the International Dateline at 70° north latitude. B) the International Dateline at 30° south latitude. C) the Greenwich meridian at 70° north latitude. D) the Greenwich meridian at 30° south latitude. E) 30° north, 120° west.
This location receives the more precipitation than any other region, for any time of year, due to orographic lifting, prevailing westerly winds, and proximity to moisture laden ocean air.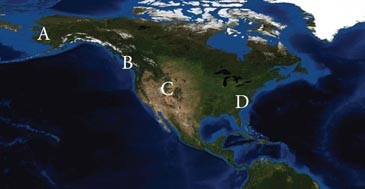
A. A B. B C. C D. D
Official temperatures are measured using thermometers placed in shelters that are
A) at ground level, in direct sunlight. B) non-ventilated and black boxes, placed at ground level. C) in black boxes placed in direct sunlight for maximum insolation absorption. D) placed a few feet above the ground in louvered white boxes.