Relative prices are an effective way of informing producers of
A) their marginal benefits of production.
B) their marginal costs of production.
C) both A and B.
D) none of the above.
C
You might also like to view...
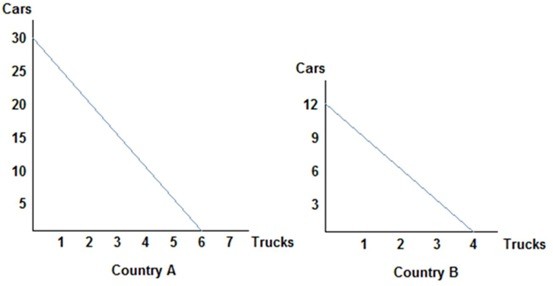 Refer to the figure shown, which represents the production possibilities frontiers for Countries A and B. Assuming both countries have the same amount of resources available to them, which of the following statements is true? Country A has:
Refer to the figure shown, which represents the production possibilities frontiers for Countries A and B. Assuming both countries have the same amount of resources available to them, which of the following statements is true? Country A has:
A. the absolute advantage in neither the production of cars nor trucks. B. an absolute advantage in the production of cars, and Country B has the absolute advantage in the production of trucks. C. an absolute advantage in the production of trucks, and Country B has the absolute advantage in the production of cars. D. the absolute advantage in the production of both cars and trucks.
The United States produces ____ of what it consumes, and consumes ____ of what it produces
a. little, little b. little, most c. most, little d. most, most
It costs a meat-processing company $50,000 to produce 5,000 pounds of steak. The company's cost will be $50,009 if it produces an additional pound of steak. If the company produces 5,001 pounds of steak then
a. its average cost is greater than its marginal cost. b. its average cost and its marginal cost are equal. c. its average cost is less than its marginal cost. d. there is insufficient information to compute average and marginal costs.
Build-Right Concrete Products produces specialty cement used in construction of highways. Build-Right is a price-setting firm and estimates the demand for its cement by the State Highway Department using a demand function in the nonlinear form:Q = aPbMc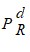 where Q = yards of cement demanded monthly, P = the price of Build-Right's cement per yard, M = state tax revenues per capita, and PR = the price of asphalt per yard. The manager at Build-Right transforms the nonlinear relation into a linear relation for estimation. The estimation results are presented below:
where Q = yards of cement demanded monthly, P = the price of Build-Right's cement per yard, M = state tax revenues per capita, and PR = the price of asphalt per yard. The manager at Build-Right transforms the nonlinear relation into a linear relation for estimation. The estimation results are presented below: 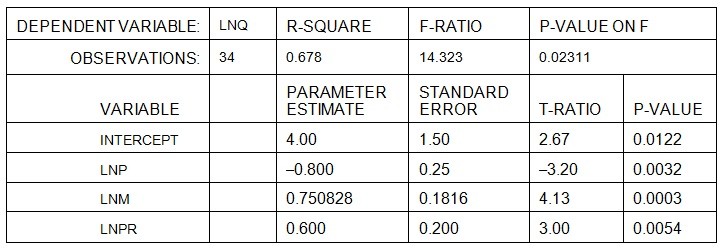
height="198" width="577" />Given the above, if the price of asphalt (PR) decreases 20%, the estimated quantity of cement demanded will: A. increase 1.2% B. increase 12% C. decrease 1.2%. D. decrease 12%. E. increase 6%