Which of the following explains economics as it should be?
a. microeconomics
b. ideal economics
c. delusional economics
d. normative economics
Ans: d. normative economics
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. The equilibrium price is ________, and the equilibrium quantity is ________. 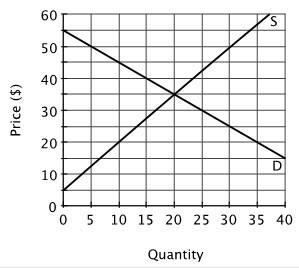
A. $30; 15 B. $35; 20 C. $25; 5 D. $25; 20
A country can gain by importing a good from abroad even if that good can be produced more efficiently at home. Is this statement true?
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following best describes how recessions are illustrated in the AD/AS diagram?
a. Recessions are illustrated in the AD/AS diagram when the equilibrium level of real GDP is substantially above potential GDP, while in years of resurgent economic growth the equilibrium will typically be close to potential GDP. b. Recessions are illustrated in the AD/AS diagram when the equilibrium level of real GDP is substantially below potential GDP, while in years of resurgent economic growth the equilibrium will typically be above potential GDP. c. Recessions are illustrated in the AD/AS diagram when the equilibrium level of real GDP is substantially below potential GDP, while in years of resurgent economic growth the equilibrium will typically be close to potential GDP. d. Recessions are illustrated in the AD/AS diagram when the equilibrium level of real GDP is substantially above potential GDP, while in years of resurgent economic growth the equilibrium will typically be below potential GDP.
Which of the following provides the best explanation of why low-income countries generally remain poor?
A. Their political environment and policies often discourage productive activity and reduce the potential gains from specialization and exchange. B. They are oppressed by developed nations that benefit from the cheap goods available from countries with low wage rates. C. They are poorly endowed with natural resources, which are essential for long-term rapid growth. D. When the average income level is low, workers have little incentive to earn higher incomes.