Suppose hamburgers and hotdogs are substitute goods. Other things constant, a rise in the price of hotdogs would tend to
A) decrease the demand for hotdogs.
B) decrease the demand for hamburgers.
C) increase the demand for hotdogs.
D) increase the demand for hamburgers.
E) do any of the above, because nobody needs hotdogs or hamburgers.
D
You might also like to view...
Deviations from interest rate parity could be due to transaction costs, differential taxation, government controls, and political risk
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
In Figure 3-5 above, saving is zero at
A) point J. B) point K. C) point L. D) none of the above because saving is never equal to zero under the conditions described in the graph.
Suppose the demand for large (and therefore high-gasoline consumption) cars decreases sharply during an energy crisis. The most likely market adjustment would be
a. a sharp rise in the price of large cars in the short run as people rush to purchase these vehicles before producers cut back on manufacturing them. b. a moderate increase in short-run prices, followed by a larger long-run price increase as the supply of large cars is depleted. c. lower short-run prices, which will lead to an expansion in the number of large cars sold. d. a decrease in the price of large cars in the short run, leading to a reduction in output, which will moderate the price decline in the long run.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 4.6 below to answer the question(s) that follow.Equilibrium in this market occurs at the intersection of curves S and D.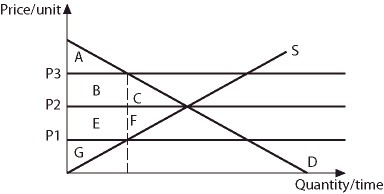 Figure 4.6Refer to Figure 4.6. If price goes from equilibrium to P1, consumer surplus changes by the area
Figure 4.6Refer to Figure 4.6. If price goes from equilibrium to P1, consumer surplus changes by the area
A. E + F. B. B - F. C. E - C. D. C + E.