What are indivisible inputs and what are their implications for economies of scale?
What will be an ideal response?
An indivisible input is something like a mold that cannot be scaled down to produce less output. Indivisible inputs are one source of economies of scale as costs per unit drop when an indivisible input is used to produce a larger output.
You might also like to view...
A firm has two customers with non-identical demands and a constant marginal cost of production. At any positive price, the consumer surplus values for the two customers are related as CS2 ? CS1
What can we say about the optimal two-part tariff for the firm? A) The firm sets the price equal to MC and the optimal tariff is equal to CS2. B) The firm sets the price equal to MC and the optimal tariff is equal to CS1. C) The firm sets the price equal to MC and the optimal tariff is equal to zero. D) The optimal price is greater than MC and the optimal tariff is equal to CS1.
A large negative output gap
a) represents a shortage of goods due to excessive demand for output b) is the result of overtime work by the labor force c) creates inflation d) means the business cycle is at a peak e) implies excessive unemployment
If the FOMC orders the sale of T-bills in the open market, then bank reserves are
A. decreased, but the money supply will remain unchanged. B. decreased, and a multiple contraction of the money supply will occur. C. increased, but the money supply will remain unchanged. D. increased, and a multiple expansion of the money supply will occur.
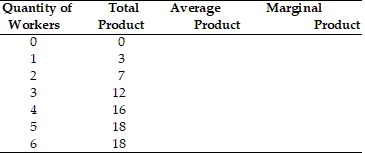 In the above table, the average physical product of 2 workers and the marginal product of the 2nd worker is
In the above table, the average physical product of 2 workers and the marginal product of the 2nd worker is
A. 4; 1. B. 3.5; 4. C. 3.5; 3.5. D. 2; 2.