A transverse periodic wave is represented by the equation y(x, t) = -1.50 cm sin(1,500 rad/s t - 10.0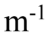 x). Another transverse wave is represented by the equation y(x, t) = +1.50 cm sin(1,500 rad/s t + 10.0
x). Another transverse wave is represented by the equation y(x, t) = +1.50 cm sin(1,500 rad/s t + 10.0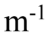 x). What is the equation that represents the superposition of the two waves?
x). What is the equation that represents the superposition of the two waves?
A. y(x, t) = 3.0 cm sin(1,500 rad/s t - 10.0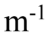 x)
x)
B. y(x, t) = 3.0 cm sin(1,500 rad/s t) cos(10.0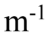 x)
x)
C. y(x, t) = +3.0 cm cos(1,500 rad/s t) sin(10.0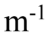 x)
x)
D. y(x, t) = 3.0 cm sin(1,500 rad/s t + 10.0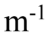 x)
x)
C. y(x, t) = +3.0 cm cos(1,500 rad/s t) sin(10.0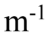 x)
x)
You might also like to view...
A banked curve in a roadway is designed for a speed of 35 mph. During an ice storm cars should be able to safely negotiate this curve at 35 mph, because at this speed
A. the necessary centripetal force is supplied entirely by the normal force from the road. B. (and at all speeds) the acceleration vector of the car points down, helping maintain stability. C. the necessary centripetal force is supplied entirely by gravity. D. the centrifugal force of the car exactly balances the centripetal force.
After a massive-star supernova, what is left behind?
A) always a white dwarf B) always a neutron star C) always a black hole D) either a white dwarf or a neutron star E) ether a neutron star or a black hole
In the normal eye the ciliary muscles that control the lens will relax
a. when viewing objects at the near point. b. when viewing objects at infinity. c. when viewing objects at a distance of 20 ft. d. only when a person has his/her eyes closed.
If one were told the object's initial velocity then one could calculate the work done by using the equations for constant acceleration to find the distance traveled. When we say work is done by a force, we mean the force does
a. all the work c. negative work b. positive work d. zero work