Indicate the order of the point mutations in the rII region.
Shown below are the maps of a series of rII- deletion strains (1–5). The deleted region is indicated as (......) and the intact region as ______. Note that strain 5 carries two different deletions.
1 ___________(...........)_______________
2 _________________(...........)_________
3 (.....................)_____________________
4 ________________________(................)
5 _____(..........)________________(.........)
rII- phage strains A-E have point mutations in the rII region. E.coli K(?) cells are coinfected with one phage that has a deletion and one phage that has a point mutation. The presence of wild-type progeny phage is assessed by the presence (+) or absence (o) of plaques.
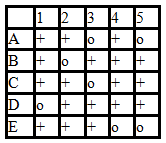
A) CADBE
B) DEBAC
C) BADCE
D) ABDEC
E) CEADB
Additional question (answer with TRUE or FALSE) :
The test described here depends on recombination.
A) CADBE
Additional answer : FALSE
You might also like to view...
Which feature is unique to echinoderms?
a. Water-vascular system b. Radial symmetry c. Cephalothorax d. Ability to regenerate body parts e. Bilateral symmetry
As DDT accumulates in the tissues of carnivores at increasing trophic levels, the concentration increases; this is representative of ________
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Transfer of genetic materials which involves sex pilus
A. Transduction B. Transformation C. Conjugation D. Transposition
A strain of Neisseria gonorrhoeae has undergone a mutation and is no longer able to make pili. Predict the most likely outcome.
A. The bacteria will become less virulent and will not be able to readily establish infection. B. The bacteria will become more virulent and will more readily establish infection. C. The bacterial strain will no longer be able to transport certain sugars into the cell. D. The bacteria will become more resistant to antibiotics.