Define the term "nonresident alien" and discuss the special tax consequences of U.S. taxation on various types of income of a nonresident alien.
What will be an ideal response?
A nonresident alien is an alien who does not have permanent residence status, (i.e., does not have a "green card" or does not meet the substantial presence test). Investment income is taxed to a nonresident alien only when it is U.S.-source income. Investment income is taxed at a 30% rate, or a reduced rate permitted by treaty. The rate is applied to the gross income amount. The U.S. payer is required to withhold from the income the amount of U.S. taxes due. A nonresident alien who owns or operates a business in the United States is taxed on his U.S. trade or business income. Income is "effectively connected" with the conduct of a U.S. trade or business if either an asset-use or business activities test is satisfied.
An alien who conducts a U.S. trade or business may have to make two separate tax calculations. Investment income that is unrelated to the U.S. trade or business is taxed at a 30% rate or at a lower rate specified in a tax treaty. The tax is collected by withholding. Business income is reduced by all related expenses and losses and taxed at the regular U.S. tax rates. Nonresident aliens cannot use the standard deduction otherwise available for individual taxpayers. They must itemize their deductions. Nonresident aliens are limited to a single personal exemption. The business income for an unmarried nonresident alien is taxed using the tax rate schedules for a single taxpayer. A married nonresident alien uses the tax rate schedule for married filing separately, unless an election to file a joint return with a U.S. resident or citizen is made. The taxes that are owed on the U.S. trade or business income can be offset by available tax credits. Business taxes are collected via estimated tax payments or when the return is filed.
You might also like to view...
The statement of cash flows is used by outside parties in all but which of the following ways?
A. To assess equity values since the firm's value is dependent on the discounted present value of its expected future cash flows. B. To assess whether to underwrite an issue of debt or equity securities, using the firm's expected operating cash flows in the analysis. C. To assess if the proper amount of income taxes is reported and can be paid from current funds. D. To assess credit risk, as cash flows provide the resources for periodic interest and principal repayment.
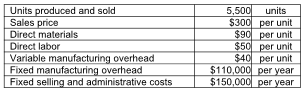
There are no beginning inventories. Prepare an income statement using the contribution margin format.
The following data has been provided by Jestina, Inc. for the year.
A major problem with sending instant messages to people is that the message
A) usually only makes sense to tech-savvy workers. B) gives the impression of the sender being disorganized. C) can be quite disruptive to the other person. D) is typically in violation of company policy.
The relevant product market includes only products that, although produced by different firms, have identical attributes
Indicate whether the statement is true or false