Under the payback method and assuming these machines are mutually exclusive, which machine(s) would Dammon Corp. choose?
The Dammon Corp. has the following investment opportunities:
Machine A Machine B Machine C
($10,000 cost) ($22,500 cost) ($35,500 cost)
Inflows Inflows Inflows
year 1 $ 6,000 year 1 $ 12,000 year 1 $ -0-
year 2 3,000 year 2 7,500 year 2 30,000
year 3 3,000 year 3 1,500 year 3 5,000
year 4 -0- year 4 1,500 year 4 20,000
A) Machine A
B) Machine B
C) Machine C
D) Machine A and B
A) Machine A
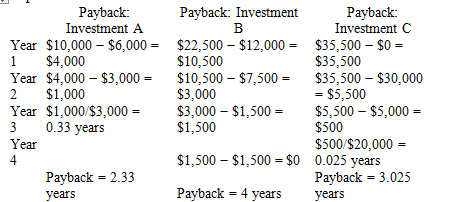
You might also like to view...
Siva has noticed a problem with his team that he manages. He has come up with a theory to explain the problem. He then tests his theory with independent and dependent variables. Siva has used what to help his critical-thinking process?
A. leadership B. the scientific method C. evidence-based management D. the open systems theory
How can the visual impact of a televised press conference be enhanced?
What will be an ideal response?
Merati Corporation has two manufacturing departments-Forming and Assembly. The company used the following data at the beginning of the year to calculate predetermined overhead rates: FormingAssemblyTotalEstimated total machine-hours (MHs) 5,000 5,000 10,000Estimated total fixed manufacturing overhead cost$28,000$10,500$38,500Estimated variable manufacturing overhead cost per MH$1.80$2.60 During the most recent month, the company started and completed two jobs-Job B and Job L. There were no beginning inventories. Data concerning those two jobs follow: Job BJob LForming machine-hours 3,400 1,600Assembly machine-hours 2,000 3,000Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments. The
manufacturing overhead applied to Job L is closest to: (Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.) A. $27,830 B. $11,840 C. $14,100 D. $25,940
As applied to bonds, duration refers to
A) the average maturity of a diversified portfolio of corporate bonds. B) the point in the life of a bond when its price risk exactly offsets its reinvestment risk. C) the average price and annual reinvestment rate of return for a bond. D) the point in the life of a bond when its yield-to-maturity equals its expected yield.